Z-Stack for Kids: Review (2023)
Z-Stack is a multivitamin developed by Dr. Vladimir Zelenko, MD — a physician known for developing the "Zelenko Protocol" for treating and preventing COVID-19. The protocol has as its centerpiece, but not exclusive piece, the combined use of Hydroxychloroquine (HCQ) and Zinc as a means by which a person can both help to prevent or mitigate the contraction of COVID-19, or can actually treat the disease once it has been diagnosed.
 |
| Z-Stack for Kids (Buy online HERE). |
He has since evolved his protocols to include a quercetin, zinc, vitamin D and C protocol for low-risk patients as well as guidelines for COVID-19 prevention.
Can children take quercetin? Most studies suggest that it’s safe to give quercetin to your child, although you should use only half the dose you'd use on an adult. Talk to your pediatrician before giving any quercetin to your child.
Pediatrician and CEO of The RIMLAND Center, Dr. Elizabeth Mumper recommends the following quercetin dosage for child, toddlers and kids (source):
In an effort to make it easier for patients, Dr Zelenko has developed an oral supplement that contains all four key ingredients: vitamin C, quercetin, vitamin D3 and zinc together. It’s referred to as 'Z-Stack Supplement'.
 |
| Z Stack for Kids |
The cost of the Z-STACK vitamin cocktail is $55 per bottle for a one month supply. Z-Stack Vitamin cocktail provides key ingredients needed in order to help your body fight off this deadly invader.
According to peer reviewed papers (R, R) on the NIH server, the use of a zinc ionophore such as quercetin and zinc has antiviral properties against covid and flu.
Dr. Zelenko has launched the Z-Stack vitamin for kids in the form of gummies, which could very well prove to be effective in the prevention and treatment of the COVID-19 in kids.
Dosages:
- 3 - 6 years: 1 gummy per day
- 6 - 9 years: 2 gummies per day
- 9 - 18 years: 3 gummies per day
The cost for Kids Z Stack Gummies is $55 per bottle (90 gummies) as well.
In this article, we review the science behind each ingredient for kids.
The Science behind Zinc, Quercetin, Vitamin D and C to Optimize the Immune System to Fight COVID-19
Recent data, from peer reviewed studies, scientific data and clinical trials show that synergistic supplement combinations involving zinc and the zinc ionophore quercetin may be effective antiviral prevention and therapeutic agents against COVID-19. An ionophore transports molecules inside cell membranes. COVID-19 viral entry and replication in cells is inhibited by zinc - significantly reducing COVID-19 infection and mortality (Source). Generally, the more zinc that can be brought into respiratory cells, the better off a COVID-19 patient will be.Quercetin, a natural anti-oxidant and anti-inflammatory compound contained in abundance in various fruits and vegetables, is a zinc ionophore. Zinc ionophores help transport zinc inside the cells COVID-19 attacks - respiratory cells, providing significant antiviral action against COVID-19.
Additionally, Quercetin has been shown to be a potent inhibitor of coronaviruses by inhibiting cellular entry as well as inhibiting proinflammatory cytokines. One of the hallmarks of COVID-19 is an imbalanced immune response cascading to cytokine storms and then hyper inflammation which then can lead to acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS).
Quercetin has been shown to inhibit proinflammatory cytokine production as well as inflammation due to its antioxidant properties, amongst others. By inhibiting destructive inflammation and potentially the entire cascade, quercetin may prevent severe damage to the respiratory system amongst other organs (source).
Quercetin has been shown to inhibit proinflammatory cytokine production as well as inflammation due to its antioxidant properties, amongst others. By inhibiting destructive inflammation and potentially the entire cascade, quercetin may prevent severe damage to the respiratory system amongst other organs (source).
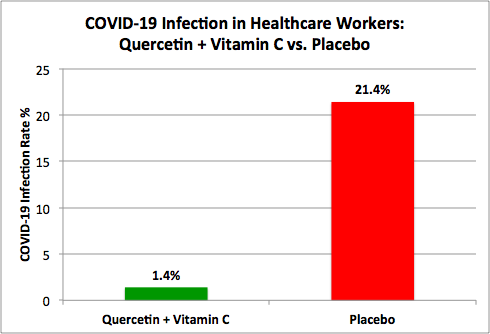
Clinical trial data shows that the combination of Vitamin C and Quercetin provided strong preventative protection against COVID-19 infection of healthcare workers when compared to the control group as shown below (source). Specifically, 1.4% (1 out of 71 healthcare workers) of healthcare workers using Quercetin and Vitamin C combination were infected with COVID-19 vs. 21.4% (9 out of 42 healthcare workers) of healthcare workers in the control group were infected with COVID-19 (Total Subjects, n = 113).
- Toddlers: up to 250 mg twice a day
- Elementary: up to 500 mg twice a day
- Adolescents: 400 - 600 mg up to three times a day
Vitamin D3 is essential to a healthy immune system as it initiates the adaptive immune response. Clinical trial data shows that Vitamin D supplementation is safe and protects against acute respiratory tract infection mortality whereas low levels of vitamin D are associated with higher risk for infection and mortality (bmj.com). In addition, a meta-analysis of COVID-19 studies shows that over 90% of studies report positive effects of Vitamin D against COVID-19 (vdmeta.com).
The link between vitamin D and viral infections arose from the observation of the seasonality of vitamin D with lower levels in the winter and concomitant increases in influenza. Conversely, in summer, serum levels of Vitamin D increase and influenza virtually disappears, except during pandemics. Even in pandemics, most deaths occur during cold months.
Daily intakes of up to 25–100 mcg (1,000 IU–4,000 IU) vitamin D in foods and dietary supplements are safe for children (depending on their age). We are expecting the dose of vitamin D3 for Z-Stack for kids to be around 50 mcg (2,000 IU) per serving. Again, this dose is way above the 100% Daily Value for kids.
Further, if your child is taking milk based products on a regular basis, most of the milk based foods and formulas are already fortified with vitamin D3. Talk to your pediatrician before giving any vitamin D3 supplement to your child especially if you are considering this on a long term basis.
Pediatrician and CEO of The RIMLAND Center, Dr. Elizabeth Mumper recommends the following doses for toddlers and kids (source):
- Infants: 400 - 800 IU/day
- Toddlers: 1000 - 2000 IU/day
- Elementary: 2000 - 4000 IU/day
- Adolescents: 4000 - 5000 IU/day
Vitamin C is a potent antioxidant, likely immune system optimizer and has been shown to work synergistically with quercetin, likely increasing quercetin’s bioavailability (source). As published in Integrative Medicine’s 4th edition, quercetin is a poorly absorbed nutrient but Vitamin C increases the absorption of quercetin and recommends that Quercetin should be blended with Vitamin C (source). Specifically, there is evidence that vitamin C and quercetin co-administration exerts a synergistic antiviral action due to overlapping antiviral and immunomodulatory properties and the capacity of ascorbate to recycle quercetin, increasing its efficacy (source). It has been shown that Quercetin and Vitamin C markedly inhibited mRNA expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines - as the release of inflammatory cytokines are behind acute respiratory distress syndrome (source). The quercetin and vitamin C combination can prevent the exacerbation of inflammation. That said, the dose of vitamin C in Z-Stack is slightly lower than what has been shown to be beneficial especially for colds and other respiratory infections. This can be resolved by having additional vitamin C through your diet.
A 2007 Cochrane review examined placebo-controlled trials involving the use of at least 200 mg/day vitamin C taken either continuously as a prophylactic treatment or after the onset of cold symptoms [source]. In the general population, use of prophylactic vitamin C modestly reduced cold duration by 8% in adults and 14% in children.
Talk to your pediatrician before giving any vitamin C supplement to your child.
Zinc is a well known supplement that is generally contained in standard multivitamins. It provides immune support amongst other functions. Zinc inhibits coronavirus replication and is a general stimulant of antiviral immunity (source). Higher levels of intracellular zinc showed to increase intracellular pH; which affect on RNA-dependent RNA polymerase and decreases the replication mechanism of RNA viruses (e.g. COVID-19). Therefore, zinc ionophores (e.g. Quercetin) can likely be used with zinc supplement to act as antiviral against many RNA viruses including influenza and COVID-19. Suggested benefits of zinc supplementation along with zinc ionophores to prevent and treat COVID-19 and other respiratory tract infections are supported by countless studies (source). In most cases, prophylactic and early use of zinc supplementation was more effective than late therapeutic proceedings. Up to 30% of the everyday respiratory infections, briefly named “common cold,” are due to infections with coronaviruses. Studies showed reduced symptom severity, reduced frequency, and duration of the common cold after zinc administration depending on dosage, zinc compound and the start time after initial symptoms (source). In conclusion, zinc supplementation is associated with a significant decrease in COVID-19 mortality as long as it is delivered with a zinc ionophore (source).
Talk to your pediatrician before giving any zinc supplement to your child.
Where to Buy Kids Z-Stack?
You can order Kids Z-Stack at Dr Zelenko's website HERE.
Note: To get 5% OFF, please use this coupon code: drfrancis



.png)
.png)

.jpg)

.png)


Comments