EECP (Enhanced External Counter Pulsation) Therapy 101: What You Need to Know 2025
 |
What is EECP
Enhanced External Counter Pulsation (EECP) is a non-invasive treatment to lower the number and intensity of angina episodes. It is an alternative solution for patients suffering from angina, who have exhausted all their other medical treatments and therapy choices.
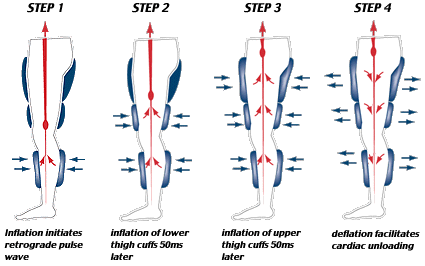
Treatment is administered through three pairs of external inflatable cuffs that are applied around the lower legs, upper legs and buttocks. A mechanism of squeeze-and-release is then synced with the heartbeat to increase blood flow to the heart and the rest of the body. Through this process, EECP generates new pathways surrounding the blocked arteries and expand the network of the small blood vessels to promote and increase blood flow towards the heart muscle. It can also be referred to as a natural bypass.
The treatment schedule includes 7 weeks of continuous treatments, which require daily visits for one hour, Monday through Friday.
Treatment is administered through three pairs of external inflatable cuffs that are applied around the lower legs, upper legs and buttocks. A mechanism of squeeze-and-release is then synced with the heartbeat to increase blood flow to the heart and the rest of the body. Through this process, EECP generates new pathways surrounding the blocked arteries and expand the network of the small blood vessels to promote and increase blood flow towards the heart muscle. It can also be referred to as a natural bypass.
In 2014, various renowned medical organisations, including the American Heart Association, Society of Cardiovascular Angiography and Interventions, and the American College of Cardiology, approved EECP as an effective treatment to cure patients suffering from angina refractory.

The treatment schedule includes 7 weeks of continuous treatments, which require daily visits for one hour, Monday through Friday.
History of EECP Treatment
EECP treatment originated in China where it has been extensively used since the 1960s. In the past 10 years it has been introduced to the United States, where there are currently around 1200 machines in operation. The idea for EECP stemmed from the development of the intra-aortic balloon pump (IABP). IABP resulted in increasing the amount of blood that can get pumped out of the heart by inflating a balloon in the aorta between each heartbeat. Opening up the aorta allows more blood flow and therefore decreases how hard the heart has to work. This same theory is applied to EECP but is taken one step further. EECP Increases the amount of blood going back to the heart, providing more blood for the heart to work with. This also decreases how hard the heart has to work but on a much greater scale, especially for people with damaged heart tissue.Who Is Eligible for EECP Treatment?
Individuals are eligible for treatment if they have:- Had coronary artery bypass (CABG) or stents placed in the coronary arteries with ongoing angina.
- Had no prior bypass or stenting but continue to suffer from angina
EECP Treatment Advantages
- A noninvasive treatment
- It's safe and well tolerated
- It's supported by available evidence (albeit imperfect) that strongly suggests the treatment is quite effective in many
- Those being treated can tell pretty definitively whether it substantially reduces angina symptoms
- Less need for anti-anginal medication.
- Increased ability to do activities without onset of symptoms.
- Ability to return to enjoyable activities.
EECP Treatment Disadvantages
- Aortic insufficiency
- Recent cardiac catheterization
- Irregular heart rhythm such as atrial fibrillation
- Severe hypertension (high blood pressure)
- Peripheral artery disease involving the legs
- A congenital heart defect
- Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
- Valvular disease
- Enlarged heart
- A pacemaker
- Pulmonary hypertension
- Heart rate over 120 beats per minute
- History of deep venous thrombosis
Find EECP Therapy Centers in USA
If you’re interested in getting an EECP therapy, check out this EECP Therapy Locator in USA. To locate International EECP® Treatment Centers, please contact VSK Medical.
.png)
.png)
.jpg)





Comments