Buffered Vs Unbuffered Vitamin C (2023)
Vitamin C may be one of the most well-known immune nutrients that protect against immune deficiencies and which supports the prevention and recovery from the common cold and upper-respiratory issues, and also protects your cardiovascular system, eyes, skin, and other parts of your body.
Buffered Vs Unbuffered Vitamin C

Unbuffered vitamin C is typically in the form of ascorbic acid. This is the purest and most common form of vitamin C which can be rapidly absorbed by the body, providing a quick boost of vitamin C when needed. However, unbuffered vitamin C in the form of ascorbic acid is highly acidic. This acidity can be harsh on the stomach for some individuals, especially when taken in high doses or on an empty stomach.
Buffered vitamin C is typically found in the form of calcium ascorbate or sodium ascorbate. These forms of vitamin C are less acidic and may be easier on the stomach. However, buffered vitamin C may have slightly slower absorption rates compared to ascorbic acid due to the presence of buffering agents. This can be beneficial for those who prefer a more sustained release of vitamin C into the bloodstream.
Is It Better to Take Buffered or Unbuffered Vitamin C?
Which one to choose depends on your specific needs and tolerance:
- Unbuffered ascorbic acid might be a good option if you want a quick vitamin C boost or are taking it to help your immune system, especially if you are able to tolerate its acidity.
- Buffered vitamin C in the form of calcium ascorbate or sodium ascorbate may be a preferable option if you have sensitive stomach or want to take vitamin C in higher doses because it is less likely to upset your stomach.
Your personal preferences and any digestive problems you may have should be taken into consideration when deciding between buffered and unbuffered vitamin C. Before making any significant changes to your supplement regimen, always seek medical advice.
Best Buffered Vitamin C Supplements
1. Sports Research Ascorbic Acid Vitamin C 1000mg
2. Nutricost Ascorbic Acid Powder (Vitamin C)

Buy on Amazon
4.7 out of 5 – more than 3,550 global ratings
Nutricost Ascorbic Acid Powder Reviews
I am up to taking 10 grams a day and it has really kicked my bronchitis! Very happy with this product, and really surprised by the size of the container! has about 950 servings and comes with a tiny one-gram scoop for portion control. Start with low doses and work your way up, the ascorbic acid will cause stomach issues. I mix mine with my morning and evening smoothies.
3. BULKSUPPLEMENTS.COM Ascorbic Acid Powder

Best Unbuffered Vitamin C
1. Ester-C Vitamin C (as ester-c calcium ascorbate)

Buy on Amazon
Ester-c 24 hour vitamin c supplement tablets for immune support offer a unique formula that stays in your system for up to 24 hours, so you have around-the-clock immune support. The metabolites in ester-c help enhance the retention of vitamin c in your white blood cells, which are a vital component of your immune system.
– this vitamin c supplement is clinically studied to last up to two times longer than regular vitamin c
– non-gmo, gluten free vegetarian vitamins are made with no artificial color, flavor, or sweetener
For adults, take two ester-c 500 mg vitamin c immune support supplements once daily, preferably with a meal.
4.8 out of 5 – more than 7,200 global ratings
Ester-c Vitamin C Immune Support Tablets Reviews
I felt a real difference using these while on iron! I used this along with other stuff in my immunity regimen and I firmly believe this works exactly as it says. Given the pandemic and working as a nurse, I wanted to strengthen my immune system as I go in and help my patients everyday. I take these every morning with orange juice, iron and elderberry drops and I believe it works great for me! Will purchase again!
2. Solgar Ester-C Plus 500 mg Vitamin C (Ascorbate Complex)

Buy on Amazon
The Vitamin C metabolites in Ester-C positively impact retention of Vitamin C in cells; This complex yields beneficial antioxidant and immune system support; Includes natural bioflavonoids, acerola berry, and rose hips fruit powder
Moreover, special manufacturing process creates a unique calcium ascorbate metabolite complex; Less acidic, pH-neutral Vitamin C for sensitive stomachs; Easy to digest, highly-absorbable
- free of: gluten, wheat, dairy, soy, yeast, sugar, sodium, artificial flavor, sweetener, and color
Ratings
4.8 out of 5 – more than 3,350 global ratings
Solgar Ester-C Plus 500 mg Vitamin C Supplement for Immune System Reviews
I use this product to help my immune system. I like that it is made of natural products. It seems to help keep bladder infections away for me. I take this so that I will not get the flu. Usually every winter I get a bad flu but this year for me I did not get the flu. I have been buying this at a local store but I like the convenience of having this delivered. We all could stand stronger immune systems.
3. Pure Encapsulations Buffered Ascorbic Acid (Calcium Ascorbate, Magnesium Ascorbate, Potassium Ascorbate)

FAQ
1. Vitamin C Benefits
a. Vitamin C is an Antioxidant
When free radicals build up in the body, they can cause oxidative stress, which has been related to a variety of chronic illnesses.
Antioxidants are molecules that help the body’s immune system function better by defending cells against dangerous molecules known as free radicals. Vitamin C is an antioxidant that can help to boost your body’s natural defenses. It protects the skin from oxidative stress by sequentially donating electrons to neutralize the free radicals. (Source)
Antioxidants are molecules that help the body’s immune system function better by defending cells against dangerous molecules known as free radicals. Vitamin C is an antioxidant that can help to boost your body’s natural defenses. It protects the skin from oxidative stress by sequentially donating electrons to neutralize the free radicals. (Source)
b. Vitamin C Helps Lower Blood Pressure
A study suggest that the antihypertensive effect of vitamin C is associated with a reduction in vascular sensitivity to noradrenaline and enhancement of endothelium-dependent relaxation due to increased nitric oxide bioavailability.
Another study also suggest that for short-term trials, vitamin C supplementation reduced systolic BP (SBP) and diastolic BP (DBP). Long-term trials on the effects of vitamin C supplementation on BP and clinical events are needed.
Another study also suggest that for short-term trials, vitamin C supplementation reduced systolic BP (SBP) and diastolic BP (DBP). Long-term trials on the effects of vitamin C supplementation on BP and clinical events are needed.
Vitamin C for Diabetes Type 2
A review of 28 studies (Diabetes Care. 2021 Feb) in 1,574 people with type 2 diabetes mellitus, demonstrated that vitamin C supplementation may improve blood sugar control and blood pressure in people with type 2 diabetes.
c. Vitamin C for the Immune System
Overall, vitamin C appears to exert a multitude of beneficial effects on cellular functions of both the innate and adaptive immune system. Although vitamin C is a potent antioxidant protecting the body against endogenous and exogenous oxidative challenges, it is likely that its action as a cofactor for numerous biosynthetic and gene regulatory enzymes plays a key role in its immune-modulating effects. [Source]
Vitamin C also plays a vital role in neutrophil function and thus essential for proper immune system response. It helps white blood cells function more effectively while protecting them from damage by potentially harmful molecules such as free radicals.
Does Vitamin C Help With Cold?
.jpg)
Controlled studies have shown that vitamin C shortens and alleviates the common cold and prevents colds under specific conditions and in restricted population subgroups.
A review of 29 studies in 11,306 people demonstrated that regularly supplementing with vitamin C at an average dose of 1–2 grams per day reduced the duration of colds by 8% in adults and 14% in children (PubMed).
The review also demonstrated that regularly taking vitamin C supplements reduced common cold occurrence in individuals under high physical stress like marathon runners and soldiers by up to 50% (PubMed, PubMed).
People who have pneumonia tend to have lower vitamin C levels, and vitamin C supplements have been shown to shorten the recovery time (PubMed, PubMed).
.jpg)
Vitamin C for Sepsis
d. Vitamin C for Respiratory Health
Vitamin C deficiency has been linked to a weakened immune system and a higher risk of respiratory infections. Vitamin C has a function in modulating an infectious agent’s resistance. As a result, vitamin C supplementation may be beneficial in preventing and treating pneumonia.
Vitamin C intake may also speed up the recovery from a sinus infection, minimize sinus inflammation, and shorten the length of a sinus infection or cold.
e. Vitamin C for Heart Health

High blood pressure, high triglyceride or LDL (bad) cholesterol levels, and low HDL (good) cholesterol levels are factors that raise the risk of heart disease. Vitamin C may assist to lower these risk factors.
A study suggest that high supplemental vitamin C intakes can reduce incidence of major coronary heart disease events.
This report shows a strong inverse correlation with blood ascorbic acid levels and all-cause mortality, including cardiovascular disease.

A study suggest that high supplemental vitamin C intakes can reduce incidence of major coronary heart disease events.
f. Vitamin C for Iron Absorption
Vitamin C intake has been shown to improve iron absorption. It binds non-heme iron and stores it in a form that’s easier for your body to absorb. (Source)
g. Vitamin C for Skin Health
i. What Does Vitamin C Do For Skin?
Vitamin C is found at high levels in the epidermis (outer layer of skin) as well as the dermis (inner layer of skin). Its cancer-fighting (antioxidant) properties, and its role in collagen production help keep your skin healthy. This is why vitamin C is one of the key ingredients found in many antiaging skin care products.
ii. Vitamin C for Collagen Synthesis
Vitamin C is important for the formation of collagen. Collagen is a protein that makes up more than 70 percent of the dry weight of your skin. Collagen can also improve skin elasticity, reduce visible wrinkles, tooth health and increase blood flow to the skin. Therefore, collagen helps to heal damaged skin and reduces the appearance of wrinkles.
Adequate vitamin C intake can also help repair and prevent dry skin. An article published in Indian Dermatology Online Journal states that, when applied topically, vitamin C can reverse the signs of photoaging like hyperpigmentation.
iii. Vitamin C Protects From Sun
Vitamin C is also an essential part of the skin’s defense system. Your skin cells use this vitamin to protect from stress caused by pollution, smoking, and UV rays. It’s actively transported to the skin, where it can act as an antioxidant and help strengthen the skin’s barriers (ScienceDirect).
Taking vitamin C orally can enhance the effectiveness of sunscreens applied to your skin for protection from the sun’s harmful UV rays. It does this by decreasing cell damage and helping the healing process of bodily wounds. Studies have also shown that taking vitamin C may shorten the time needed for wounds to heal. (PubMed, PubMed).
h. Vitamin C for Anti-Aging
Vitamin C can help to maintain a proper epigenome, especially in combination with another longevity ingredient, alpha- ketoglutarate.
2. Vitamin C Dosage
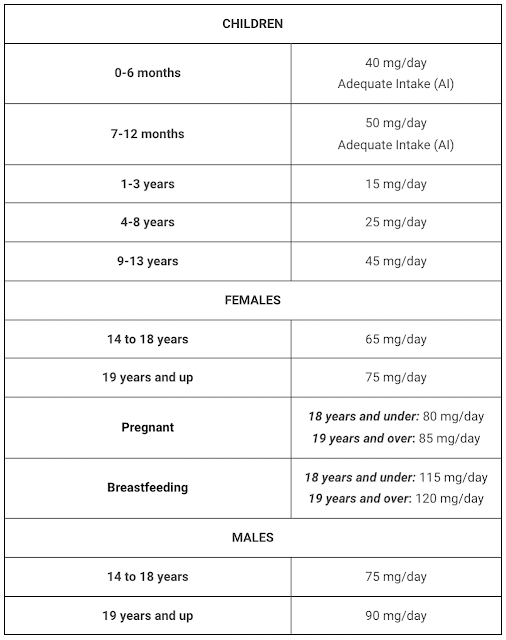
The recommended daily amount of vitamin C for adults is 90 mg for men, 75 mg for women, and up to 120 mg for women who are pregnant or breastfeeding. However, certain medical conditions may require that you take much higher doses (NIH). However, smokers need 35 mg/day more vitamin C than nonsmokers. (Source)
Children have lower vitamin C requirements, which range from 25–75mg per day, depending on their age. However, it’s not generally advised to give children a vitamin C supplement unless their pediatrician has recommended it.
Note that the Tolerable Upper Intake Level (UL) for vitamin C for men, as well as women ages 19 and above, is 2,000 mg. Meanwhile, the UL for children ranges from 400–1,800 mg, depending on age. Daily intakes at or below these amounts are unlikely to result in any adverse health effects (NIH).
Generally, high doses of vitamin C are unnecessary and could contribute to harmful side effects. Only consume high doses if your healthcare provider recommends doing so.

Children have lower vitamin C requirements, which range from 25–75mg per day, depending on their age. However, it’s not generally advised to give children a vitamin C supplement unless their pediatrician has recommended it.
Note that the Tolerable Upper Intake Level (UL) for vitamin C for men, as well as women ages 19 and above, is 2,000 mg. Meanwhile, the UL for children ranges from 400–1,800 mg, depending on age. Daily intakes at or below these amounts are unlikely to result in any adverse health effects (NIH).
Generally, high doses of vitamin C are unnecessary and could contribute to harmful side effects. Only consume high doses if your healthcare provider recommends doing so.
3. Vitamin C Deficiency
Although vitamin C deficiency is rare in developed countries, it can cause serious health problems that, if left untreated, could be fatal. Most people do not take 5 servings of fruits and vegetables on a daily basis. Furthermore, Vitamin C is easily destroyed by heat during cooking and our human bodies are not capable of producing and storing Vitamin C.
Severe vitamin c deficiency, often called scurvy, can cause bruise, gum and dental problems, dry hair and skin, also anemia. Doctor will do the diagnosis based on symptoms and blood test result. Increasing consumption of food high in vitamin c or taking vitamin C supplements usually increase your vitamin c level.
a. Risk Factors of Vitamin C Deficiency
Vitamin C levels have been shown to decrease in the elderly population as well as those exhibiting chronic underlying conditions (e.g. diabetes, hypertension).
– Alcoholism
– Babies only fed cow’s milk
– Seniors only consuming tea and toast diet
– Not getting enough fruits and vegetables
– Smokers : Tobacco smoking (each cigarette oxidizes about 60 mg of vitamin C)
– People with eating disorders
– People with type 1 diabetes who need a lot of vitamin C
– Individuals with disorders of the GI tract like inflammatory bowel disease.
– Individuals with iron overload, which causes the kidneys to waste vitamin C
– Babies only fed cow’s milk
– Seniors only consuming tea and toast diet
– Not getting enough fruits and vegetables
– Smokers : Tobacco smoking (each cigarette oxidizes about 60 mg of vitamin C)
– People with eating disorders
– People with type 1 diabetes who need a lot of vitamin C
– Individuals with disorders of the GI tract like inflammatory bowel disease.
– Individuals with iron overload, which causes the kidneys to waste vitamin C
b. Symptoms of Vitamin C Deficiency
Symptoms of vitamin C deficiency can start to appear after 8 to 12 weeks. Early signs include a loss of appetite, weight loss, fatigue, irritability, and lethargy.
Within 1 to 3 months, there may be signs of..
- Anemia
- Myalgia, or pain, including bone pain
- Swelling, or edema
- Petechiae, or small red spots resulting from bleeding under the skin
- Corkscrew hairs
- Gum disease and loss of teeth
- Poor wound healing
- Shortness of breath
- Mood changes, and depression (Source)
Within 1 to 3 months, there may be signs of..
- Anemia
- Myalgia, or pain, including bone pain
- Swelling, or edema
- Petechiae, or small red spots resulting from bleeding under the skin
- Corkscrew hairs
- Gum disease and loss of teeth
- Poor wound healing
- Shortness of breath
- Mood changes, and depression (Source)
4. Vitamin C Overdose

Vitamin C is a water soluble vitamin which gets excreted in the urine when consumed in excess.

a. How Much Vitamin C Is Too Much?
b. Vitamin C Side Effects
Although too much dietary vitamin C is unlikely to be harmful, an overdose of vitamin C supplements might cause..
- Diarrhea
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Heartburn
- Abdominal cramps
- Headache
- Insomnia
(Source)
High dose vitamin C supplements may even cause diarrhea, as they can signal your body to pull water out of the cells and into your digestive tract (NIH).
- Diarrhea
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Heartburn
- Abdominal cramps
- Headache
- Insomnia
c. Is Vitamin C Bad for Your Kidneys?
Too much vitamin C in your system can raise the amount of oxalate in your kidneys, which can lead to kidney stones.
d. Vitamin C Interactions
i. Copper
Taking large doses of vitamin C (ascorbic acid) on a regular basis lowers your level of copper, so if you are already deficient in copper and take high doses of vitamin C, you can compromise your immune system.
5. Vitamin C Foods
Fruits and vegetables are the best sources of vitamin C. Citrus fruits, tomatoes and tomato juice, and potatoes are major contributors of vitamin C to the American diet. Other good food sources include red and green peppers, kiwifruit, broccoli, strawberries, Brussels sprouts, and cantaloupe. Although vitamin C is not naturally present in grains, it is added to some fortified breakfast cereals.
The vitamin C content of food may be reduced by prolonged storage and by cooking because ascorbic acid is water soluble and is destroyed by heat. Steaming or microwaving may lessen cooking losses. Fortunately, many of the best food sources of vitamin C, such as fruits and vegetables, are usually consumed raw.
Consuming five varied servings of fruits and vegetables a day can provide more than 200 mg of vitamin C.
Obtaining nutrients from whole foods is always the best approach, but if you have difficulty meeting your nutrition needs for any reason, a supplement may be necessary.
a. Vitamin C Content in Foods
Food Serving size Mg per serving Percent of 90 mg DV Guava, raw 1 cup, raw 377 419% Sweet red pepper, raw 1 cup, raw 190 211% Tomato juice 1 cup, canned 170 188.9% Orange juice 1 cup 124 137.8% Sweet green pepper 1 cup, raw 120 133% Hot green chili pepper, raw 1 pepper, raw 109 121% Oranges 1 large fruit 97.5 108.8% Strawberries 1 cup, sliced 97.6 108% Papaya 1 small fruit 95.6 106.2% Pink grapefruit juice 1 cup 93.9 104.3% Broccoli 1 cup, raw 81.2 90.2% Pineapple chunks 1 cup, raw 78.9 87.7% Potato 1 large vegetable 72.7 80.8% Brussels sprouts 1 cup, raw 74.8 79.8% Kiwifruit 1 fruit 64 71.1% Mango 1 cup, raw 60.1 66.7% Cantaloupe 1 cup 57.3 63.7% Cauliflower 1 cup, raw 51.6 57.3% Lemon 1 fruit 44.5 49.4% White grapefruit ½ medium fruit 39 43.3%
| Food | Serving size | Mg per serving | Percent of 90 mg DV |
| Guava, raw | 1 cup, raw | 377 | 419% |
| Sweet red pepper, raw | 1 cup, raw | 190 | 211% |
| Tomato juice | 1 cup, canned | 170 | 188.9% |
| Orange juice | 1 cup | 124 | 137.8% |
| Sweet green pepper | 1 cup, raw | 120 | 133% |
| Hot green chili pepper, raw | 1 pepper, raw | 109 | 121% |
| Oranges | 1 large fruit | 97.5 | 108.8% |
| Strawberries | 1 cup, sliced | 97.6 | 108% |
| Papaya | 1 small fruit | 95.6 | 106.2% |
| Pink grapefruit juice | 1 cup | 93.9 | 104.3% |
| Broccoli | 1 cup, raw | 81.2 | 90.2% |
| Pineapple chunks | 1 cup, raw | 78.9 | 87.7% |
| Potato | 1 large vegetable | 72.7 | 80.8% |
| Brussels sprouts | 1 cup, raw | 74.8 | 79.8% |
| Kiwifruit | 1 fruit | 64 | 71.1% |
| Mango | 1 cup, raw | 60.1 | 66.7% |
| Cantaloupe | 1 cup | 57.3 | 63.7% |
| Cauliflower | 1 cup, raw | 51.6 | 57.3% |
| Lemon | 1 fruit | 44.5 | 49.4% |
| White grapefruit | ½ medium fruit | 39 | 43.3% |












Comments