Chlorella vs Spirulina vs Chlorophyll vs Chlorophyllin Comparison
Contents
1. What is Chlorella?
2. What is Spirulina?
3. What is Chlorophyll?
4. What is Chlorophyllin?
5. Chlorella vs Spirulina
6. Chlorella vs Spirulina vs Chlorophyll
7. Chlorophyll vs Chlorophyllin
2. What is Spirulina?
3. What is Chlorophyll?
4. What is Chlorophyllin?
5. Chlorella vs Spirulina
6. Chlorella vs Spirulina vs Chlorophyll
7. Chlorophyll vs Chlorophyllin
8. Euglena vs Spirulina vs Chlorella
1. What is Chlorella?
Chlorella is a green unicellular alga. There are around 30 different species of chlorella, but the two most often used in research are Chlorella vulgaris and Chlorella pyrenoidosa.
It is high in nutrients and contains a variety of vitamin and minerals. New research suggests that it may aid in the removal of toxins from the body, as well as improve cholesterol and blood sugar levels, among other health benefits.
a. What vitamins and minerals are in chlorella?
Chlorella products contain a large amount of proteins, dietary fibers, and polyunsaturated fatty acids, including α-linolenic and linoleic acids. In particular, Chlorella products contain vitamins D2 and B12, which are absent from plant-derived food sources, and larger amounts of folate and iron than other plant-derived foods. (Source)
Their high levels of polyunsaturated fat gives them very high levels of antioxidants. These are substances that interact with free radicals in your body and neutralize them, preventing cell and tissue damage.
Chlorella supplementation improves total cholesterol, low-density lipoprotein cholesterol, systolic blood pressure, diastolic blood pressure, and fasting blood glucose levels, according to a meta-analysis of the effects of Chlorella supplementation on cardiovascular risk factors. (Source)
Their high levels of polyunsaturated fat gives them very high levels of antioxidants. These are substances that interact with free radicals in your body and neutralize them, preventing cell and tissue damage.
Chlorella supplementation improves total cholesterol, low-density lipoprotein cholesterol, systolic blood pressure, diastolic blood pressure, and fasting blood glucose levels, according to a meta-analysis of the effects of Chlorella supplementation on cardiovascular risk factors. (Source)
2. What is Spirulina?
Spirulina is a blue-green alga which also has many nutrients. It includes phycocyanin, a strong plant-based protein. This has antioxidant, pain-relieving, anti-inflammatory, and brain-protective properties, according to research.
Several clinical trials also indicated that Spirulina has positive effects in managing metabolic syndrome components. (Source)
a. What vitamins and minerals are in spirulina?
In humans, this alga provides an important staple food with any significant side effects. Apart from the high protein content (up to 70%), it also contains vitamins, particularly B12 and provitamin A (-carotenes), as well as minerals, especially iron. It also contains phenolic acids, tocopherols, and -linolenic acid in abundance. Since spirulina lacks cellulose cell walls, it is easily digestible. (Source)
Spirulina contains several active ingredients, notably phycocyanin and β-carotene that have potent antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities. (Source)
Chlorophyll is located in a plant’s chloroplasts, which are tiny structures in a plant’s cells. Chlorophyll is a key component in the process of photosynthesis, which sustains plant life and produces oxygen for the entire planet. (Source)
Green vegetables are known to provide many health benefits, including antioxidant, anti-mutagenic, and detoxifying activities. A study investigated the anti-oxidative and anti-aging properties of chlorophyll in vivo using the model system Caenorhabditis elegans. And it shown that chlorophyll significantly improves resistance to oxidative stress. (Source)
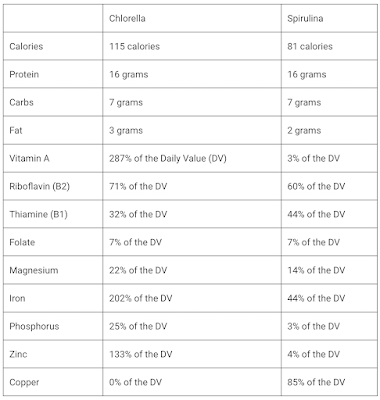
From the table above, we can conclude that both protein, carbohydrate, and fat composition are quite similar. But there are significant nutritional variances in their calorie, vitamin, and mineral amounts.
Chlorella has a high concentration of omega-3 fatty acids, vitamin A, riboflavin, iron, and zinc. Spirulina has more thiamine, copper, and potentially more protein.
Another study also found that antioxidant status and lipid profile of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) patients are proven to be improved through an interventional 2 months course of spirulina. Oxidative stress is shown to be reduced as a result of spirulina intervention.
ii. Detoxification
Plants have two forms of chlorophyll: chlorophyll a and chlorophyll b. These two kinds can be found in all plants. Both are fat-soluble compounds with antioxidant effects. Even chlorophyll is not as powerful as those found in other nutrients such as vitamins C and E, according to several research, eating leafy green vegetables on a daily basis still can help to enhance antioxidants in the bloodstream.
b. Surgery
Blue-green algae may reduce blood sugar levels during surgery. Best to stop using blue-green algae at least 2 weeks before a scheduled surgery.
Spirulina contains several active ingredients, notably phycocyanin and β-carotene that have potent antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities. (Source)
3. What is Chlorophyll?
Chlorophyll is located in a plant’s chloroplasts, which are tiny structures in a plant’s cells. Chlorophyll is a key component in the process of photosynthesis, which sustains plant life and produces oxygen for the entire planet. (Source)
Green vegetables are known to provide many health benefits, including antioxidant, anti-mutagenic, and detoxifying activities. A study investigated the anti-oxidative and anti-aging properties of chlorophyll in vivo using the model system Caenorhabditis elegans. And it shown that chlorophyll significantly improves resistance to oxidative stress. (Source)
a. What vitamins and minerals are in chlorophyll?
Vitamins A, C, E, and K, as well as antioxidants and minerals such as Magnesium, Iron, and Calcium, are abundant in chlorophyll. Chlorophyll extracts derived from plants are often available in liquid or powder form.
4. What is Chlorophyllin?
Chlorophyllin is made from chlorophyll and is often sold as an herbal supplement.
Chlorophyllin (CHL), the sodium-copper salt and the water-soluble analogue of the ubiquitous green pigment chlorophyll, has been attributed to have several beneficial properties. (Source)
Chlorophyllin is a powerful antioxidant that protects mitochondria from oxidative damage caused by a variety of reactive oxygen species. It may also prevent the body from absorbing certain chemicals that can raise a person’s cancer risk.
Chlorophyllin may aid to reduce the odor of urine or feces (bowel movements). Chlorophyllin is used to help persons with fecal incontinence caused by a spinal cord injury, bowel cancer, psychotic disorder, terminal disease, or other conditions enhance their quality of life. People who have undergone a colostomy or ileostomy utilize chlorophyllin as well. (Source)
Chlorophyllin (CHL), the sodium-copper salt and the water-soluble analogue of the ubiquitous green pigment chlorophyll, has been attributed to have several beneficial properties. (Source)
Chlorophyllin is a powerful antioxidant that protects mitochondria from oxidative damage caused by a variety of reactive oxygen species. It may also prevent the body from absorbing certain chemicals that can raise a person’s cancer risk.
Chlorophyllin may aid to reduce the odor of urine or feces (bowel movements). Chlorophyllin is used to help persons with fecal incontinence caused by a spinal cord injury, bowel cancer, psychotic disorder, terminal disease, or other conditions enhance their quality of life. People who have undergone a colostomy or ileostomy utilize chlorophyllin as well. (Source)
5. Chlorella vs Spirulina

From the table above, we can conclude that both protein, carbohydrate, and fat composition are quite similar. But there are significant nutritional variances in their calorie, vitamin, and mineral amounts.
Chlorella has a high concentration of omega-3 fatty acids, vitamin A, riboflavin, iron, and zinc. Spirulina has more thiamine, copper, and potentially more protein.
a. Benefits of Chlorella and Spirulina
i. Chlorella and Spirulina are great antioxidants.
Although they have different amount of minerals and vitamins, still, both are great antioxidant because they have high levels of polyunsaturated fat.
A study found that chlorella supplementation resulted in the conservation of plasma antioxidant nutrient status and improvement in erythrocyte antioxidant enzyme activities in subjects.
A study found that chlorella supplementation resulted in the conservation of plasma antioxidant nutrient status and improvement in erythrocyte antioxidant enzyme activities in subjects.
Another study also found that antioxidant status and lipid profile of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) patients are proven to be improved through an interventional 2 months course of spirulina. Oxidative stress is shown to be reduced as a result of spirulina intervention.
ii. Detoxification
Both algae have been shown to be successful in detoxification; they may be used in high dosages for heavy metal detox, binding toxins and purging them from the body, frequently without the usual detoxification side effects.
6. Chlorella vs Spirulina vs Chlorophyll
Despite their close relationship, chlorella, spirulina and chlorophyll are different.
Chlorella and Spirulina are both algae.
Both chlorella and spirulina contain chlorophyll, the component that gives it its color. Chlorophyll is the substance that plants use in the photosynthesis process; plants catch light and convert it to energy or food. Chlorella is known for having a higher concentration of chlorophyll than spirulina.
Chlorella and Spirulina are both algae.
Both chlorella and spirulina contain chlorophyll, the component that gives it its color. Chlorophyll is the substance that plants use in the photosynthesis process; plants catch light and convert it to energy or food. Chlorella is known for having a higher concentration of chlorophyll than spirulina.
a. Benefits of Chlorophyll
Chlorophylls mediate changes in the redox status of pancreatic cancer cells, which may be responsible for their anticancer actions and contribute to the lower cancer incidence found in clinical trials among green vegetable consumers. (Source)Plants have two forms of chlorophyll: chlorophyll a and chlorophyll b. These two kinds can be found in all plants. Both are fat-soluble compounds with antioxidant effects. Even chlorophyll is not as powerful as those found in other nutrients such as vitamins C and E, according to several research, eating leafy green vegetables on a daily basis still can help to enhance antioxidants in the bloodstream.
b. How much chlorophyll is in chlorella?
Chlorophyllin is a semi-synthetic mixture of sodium copper salts derived from chlorophyll. During the synthesis of chlorophyllin, the magnesium atom at the center of the ring is replaced with copper and the phytol tail is lost. (Source)
Chlorophyll is a fat-soluble compound, whereas Chlorophyllin is a semi-synthetic, water-soluble compound that is often used as an additive in medicines or food coloring.


source: lpi.oregonstate.edu
Chlorophyll and chlorophyllin are able to form tight molecular complexes with certain chemicals known or suspected to cause cancer, including polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons found in tobacco smoke, some heterocyclic amines found in cooked meat, and aflatoxin-B1 (Source).
Chlorophyll is a fat-soluble compound, whereas Chlorophyllin is a semi-synthetic, water-soluble compound that is often used as an additive in medicines or food coloring.


source: lpi.oregonstate.edu
Chlorophyll and chlorophyllin are able to form tight molecular complexes with certain chemicals known or suspected to cause cancer, including polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons found in tobacco smoke, some heterocyclic amines found in cooked meat, and aflatoxin-B1 (Source).
8. Euglena vs Spirulina vs Chlorella?
Absorption rate: Euglena has no cell wall, so the digestion and absorption rate is very high. Both spirulina and chlorella have cell walls, and the absorption rate is lower than that of euglena.
Nutritional ingredients: Euglena has β-1,3-glucan, which can help improve constipation; it also contains DHA and EPA which are almost not found in spirulina and chlorella.
Safety: Chlorella has a high content of pheophytin, which is easy to cause photosensitivity. Spirulina is easily contaminated by toxins and heavy metals, and is a multicellular algae with high nucleic acid content, which is not friendly to gout patients. Euglena is a freshwater algae, which does not have the above-mentioned problems, and has a low pheophytin content, which is unlikely to cause photosensitivity.
Euglena is cultivated in freshwater by Ulve, which is a very critical point. Therefore, Euglena does not contain iodine. (Source)
Nutritional ingredients: Euglena has β-1,3-glucan, which can help improve constipation; it also contains DHA and EPA which are almost not found in spirulina and chlorella.
Safety: Chlorella has a high content of pheophytin, which is easy to cause photosensitivity. Spirulina is easily contaminated by toxins and heavy metals, and is a multicellular algae with high nucleic acid content, which is not friendly to gout patients. Euglena is a freshwater algae, which does not have the above-mentioned problems, and has a low pheophytin content, which is unlikely to cause photosensitivity.
Euglena is cultivated in freshwater by Ulve, which is a very critical point. Therefore, Euglena does not contain iodine. (Source)
FAQs
1. Who should not take chlorella?
Warfarin and other blood-thinning medications may have a tougher time working if you eat chlorella.
Iodine allergies should avoid chlorella supplements since some of them include iodine. Best to inform your doctor about any supplements you are taking.
2. Who should not take spirulina?
Iodine allergies should avoid chlorella supplements since some of them include iodine. Best to inform your doctor about any supplements you are taking.
2. Who should not take spirulina?
a. Autoimmune disease
Multiple sclerosis (MS), lupus (systemic lupus erythematosus, SLE), rheumatoid arthritis (RA), pemphigus vulgaris (a skin ailment), and others are autoimmune illnesses. The immune system may become more active as a result of blue-green algae, which might worsen the symptoms of auto-immune diseases. It’s advised to avoid utilizing blue-green algae if you have one of these diseases.b. Surgery
Blue-green algae may reduce blood sugar levels during surgery. Best to stop using blue-green algae at least 2 weeks before a scheduled surgery.
c. Bleeding conditions / Using blood thinners
Spirulina has an anticoagulant effect, which means it thins your blood and makes it take longer for blood to clot. If you have a bleeding condition or are using blood thinners, you should avoid spirulina.3. Who should not take chlorophyll?
If your doctor has prescribed this medicine, your doctor or pharmacist may already be aware of any potential drug interactions. Before starting, stopping, or changing the dosage of any medication, consult your doctor, health care provider, or pharmacist.
There are no known severe, serious, moderate, or mild interactions between chlorophyll and other medications.
This list does not include all potential interactions or side effects. As a result, inform your doctor or pharmacist of all the drugs you consume before taking this medication.
There are no known severe, serious, moderate, or mild interactions between chlorophyll and other medications.
This list does not include all potential interactions or side effects. As a result, inform your doctor or pharmacist of all the drugs you consume before taking this medication.
You May Be Interested In:
Cilantro and Chlorella for Heavy Metal Detox

.png)
.png)


.png)
.jpg)




Comments