Vitamin C 101: What You Need to Know (2022)
Contents
1. What is Vitamin C2. Types of Vitamin C
3. Types of Vitamin C Supplement
4. Vitamin C and Other Supplements
5. Vitamin C Benefits
5. Vitamin C Benefits
6. Vitamin C Dosage
7. Vitamin C Deficiency
8. Vitamin C Overdose
9. Vitamin C Foods
10. Vitamin C and Covid-19
7. Vitamin C Deficiency
8. Vitamin C Overdose
9. Vitamin C Foods
10. Vitamin C and Covid-19
11. Online Shopping Guide

Vitamin C is an essential nutrient which cannot be produced by humans (Nutrients. 2017). Because your body doesn’t produce or store it, you need daily vitamin C for continued health. Vitamin C may be one of the most well-known immune nutrients that protect against immune deficiencies and which supports the prevention and recovery from the common cold and upper-respiratory issues, and also protects your cardiovascular system, eyes, skin, and other parts of your body.
Vitamin C is a particularly unique nutrient because it also functions as an antioxidant that protects your cells against potential damage.
However, steady state comparative bioavailability studies in humans have shown no differences between synthetic and natural vitamin C, regardless of the subject population, study design or intervention used.
Take a look at added ingredients, too. If you’re trying to limit your intake of added sugars, you want to opt for a supplement that doesn’t contain sugar.
Children have lower vitamin C requirements, which range from 25–75mg per day, depending on their age. However, it’s not generally advised to give children a vitamin C supplement unless their pediatrician has recommended it.
Generally, high doses of vitamin C are unnecessary and could contribute to harmful side effects. Only consume high doses if your healthcare provider recommends doing so.
However, certain people, especially those with stomach acid concerns, may find it difficult to digest due to its small acidic component. While ascorbic acid is manufactured synthetically, it is equivalent to natural forms. Because studies have shown that only 30% of a given dosage is actually absorbed, researchers have looked for different formulations that would be more easily absorbed in the gastrointestinal system.

Vitamin C is a potent antioxidant, likely immune system optimizer and has been shown to work synergistically with quercetin, likely increasing quercetin’s bioavailability (source). As per Integrative Medicine’s 4th edition, quercetin is a poorly absorbed nutrient but Vitamin C increases the absorption of quercetin and recommends that Quercetin should be blended with Vitamin C (source).
Antioxidants are molecules that help the body’s immune system function better by defending cells against dangerous molecules known as free radicals. Vitamin C is an antioxidant that can help to boost your body’s natural defenses. It protects the skin from oxidative stress by sequentially donating electrons to neutralize the free radicals. (Source)
Another study also suggest that for short-term trials, vitamin C supplementation reduced systolic BP (SBP) and diastolic BP (DBP). Long-term trials on the effects of vitamin C supplementation on BP and clinical events are needed.
.jpg)
Severe vitamin c deficiency, often called scurvy, can cause bruise, gum and dental problems, dry hair and skin, also anemia. Doctor will do the diagnosis based on symptoms and blood test result. Increasing consumption of food high in vitamin c or taking vitamin C supplements usually increase your vitamin c level.
– Alcoholism
– Babies only fed cow’s milk
– Seniors only consuming tea and toast diet
– Not getting enough fruits and vegetables
– Smokers : Tobacco smoking (each cigarette oxidizes about 60 mg of vitamin C)
– People with eating disorders
– People with type 1 diabetes who need a lot of vitamin C
– Individuals with disorders of the GI tract like inflammatory bowel disease.
– Individuals with iron overload, which causes the kidneys to waste vitamin C

In males and females aged 19 years and older, the upper limit for vitamin C consumption is 2,000 mg. For pregnant or nursing women, the restriction stays the same.
Safety: The U.S. Recommended Dietary Allowance (RDA) for vitamin C is 75 to 120 milligrams per day. Taking large doses of vitamin C (ascorbic acid) on a regular basis lowers your level of copper, so if you are already deficient in copper and take high doses of vitamin C, you can compromise your immune system.
Temporarily taking megadoses of vitamin C supplements to combat a case of the cold or flu is likely not going to cause a problem.
Many vitamin C supplements that are above the US RDA are sold in the market. It’s important to seek a physician’s advice if you intend to take high dose vitamin C on a long term basis. To be on the safe side, you may also request for your kidney functions to be monitored.
For long-term, daily use, your best bet is to eat a diet that is full of high quality organic vegetables and fruits that are minimally processed. Not only will you get vitamin C, but you will get all the other accessory nutrients and micronutrients that are needed to optimize it.
It is also recommended to monitor your oxygen saturation with a pulse oximeter and to go to the hospital if you get below 94%. The medical evidence to support each drug and nutrient can be found under “Medical Evidence” on the FLCCC’s website.
1. Elemental Zinc 25mg 1 time a day (PubMed) (Amazon)

1. What is Vitamin C?

Vitamin C is a particularly unique nutrient because it also functions as an antioxidant that protects your cells against potential damage.
a. Organic Vitamin C vs Synthetic Vitamin C
Organic Vitamin C is the whole food vitamin C that occurs in its natural state. Vitamin C in this form contains bioflavonoids. Synthetic vitamin C is an isolated version of vitamin C. It is devoid of the micronutrients, dietary fiber and phytochemicals like bioflavonoids found in vitamin-rich wholefoods.
Bioflavonoids are antioxidants that enhance the use of vitamin C by improving its absorption and prolonging its effectiveness. Flavonoids themselves provide many health benefits. They are collectively referred to as "vitamin P" in recognition of their antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, antiallergenic, antiviral, and anti-carcinogenic properties.
i. Is Natural Vitamin C Better Than Synthetic?
Yes. Natural Vitamin C is less processed, more whole, more active, more readily absorbed, and less toxic than the synthetic isolate.
b. How To Choose The Right Vitamin C
Selecting the right vitamin C supplement depends on a variety of factors, including the form, quality, dose, and price.a. Form
You can start by considering how you’ll be using the supplement. For instance, if you prefer to take a pill, you’ll want to check out encapsulated vitamin C supplements. If you don’t like swallowing pills or want to mix it into beverages, your best bet is to consider liquid or powdered supplements.b. Quality
Evaluate whether a brand is reputable by exploring their ingredient sourcing and manufacturing standards. A good product will also be tested by third-party organizations, such as USP, Consumer Labs, or NSF International.Take a look at added ingredients, too. If you’re trying to limit your intake of added sugars, you want to opt for a supplement that doesn’t contain sugar.
c. Dosage
The recommended daily amount of vitamin C for adults is 90 mg for men, 75 mg for women, and up to 120 mg for women who are pregnant or breastfeeding. However, certain medical conditions may require that you take much higher doses (NIH).Children have lower vitamin C requirements, which range from 25–75mg per day, depending on their age. However, it’s not generally advised to give children a vitamin C supplement unless their pediatrician has recommended it.
Generally, high doses of vitamin C are unnecessary and could contribute to harmful side effects. Only consume high doses if your healthcare provider recommends doing so.
d. Budget
Some professional-grade brands can be expensive, but keep in mind that a higher price doesn’t necessarily mean a better product. There are plenty of high quality options available at various price points.2. Types of Vitamin C
a. Ascorbic Acid Vitamin C
Doctor's Best Vitamin C with QC Ascorbic Acid 1000 mg - Best Vitamin C with Ascorbic Acid
Ascorbic acid is the cheapest form of vitamin C and the type that is used the most often. Ascorbic acid comes in the form of pills, capsules, or powder.However, certain people, especially those with stomach acid concerns, may find it difficult to digest due to its small acidic component. While ascorbic acid is manufactured synthetically, it is equivalent to natural forms. Because studies have shown that only 30% of a given dosage is actually absorbed, researchers have looked for different formulations that would be more easily absorbed in the gastrointestinal system.
Mineral Ascorbates
b. Calcium Ascorbate Vitamin C
Natural Factors, Bioactive Quercetin - Calcium Ascorbate Vitamin C with Quercetin
Calcium Ascorbate generates less gastrointestinal discomfort than ascorbic acid formation while keeping the same antioxidant capacity. This formula contains both calcium (90-100 mg) and ascorbate (900 mg) which will help increase bone health and prevent osteopenia and osteoporosis.
Bioflavonoids are a group of compounds present in many of foods that are high in vitamin C. In fact, scientists have discovered over 8,000 different bioflavonoid structures in nature. The natural pigments that give fruits and vegetables their color are bioflavonoids (also known as flavonoids).
Vitamin C is frequently mixed with bioflavonoids, which are antioxidants. Bioflavonoids are said to help Vitamin C absorption. It’s a good choice for anyone who are sensitive to ascorbic acid’s gastrointestinal side effects.
c. Magnesium Ascorbate Vitamin C
Magnesium ascorbate is great for those with low magnesium, persistent headaches or leg cramps. It consists of ascorbate and magnesium (50-100mg).d. Sodium Ascorbate Vitamin C
NOW Supplements, Sodium Ascorbate Powder - Sodium Ascorbate Vitamin C
This supplement includes sodium (100-200 mg) and ascorbate (900 mg). This formulation should be avoided by anyone on a low-salt diet. While most low-salt dieters should limit their daily salt intake to less than 2,000 mg, even little quantities can pile up over time.e. Vitamin C with Bioflavonoids
Viva Naturals Vitamin C - Vitamin C Supplement with Bioflavonoids
What is bioflavonoids?Bioflavonoids are a group of compounds present in many of foods that are high in vitamin C. In fact, scientists have discovered over 8,000 different bioflavonoid structures in nature. The natural pigments that give fruits and vegetables their color are bioflavonoids (also known as flavonoids).
Vitamin C is frequently mixed with bioflavonoids, which are antioxidants. Bioflavonoids are said to help Vitamin C absorption. It’s a good choice for anyone who are sensitive to ascorbic acid’s gastrointestinal side effects.
f. Liposomal Vitamin C
Nutrivein Liposomal Vitamin C 1650mg - Best Liposomal Vitamin C
Liposomes are incredibly tiny particles resembling our cells that bypasses the digestive system.
Liposomal vitamins don’t use capsules or tablets or powders to deliver nutrients. Instead, the vitamins are encapsulated in pockets of fat cells called liposomes (hence the name). Apparently this is the most effective way of ensuring the vitamins in the supplement actually get absorbed into your body.
The key distinction between liposomal Vitamin C and conventional Vitamin C is its bioavailability. Because typical Vitamin C is water soluble, its bioavailability is quite poor. When taken orally, only approximately 12 percent to 14 percent of conventional Vitamin C is absorbed.
Vitamin C, on the other hand, is transported straight into the cells of the body in its liposomal form, without being destroyed or expending energy in the process, maximizing its effect.

Vitamin C, on the other hand, is transported straight into the cells of the body in its liposomal form, without being destroyed or expending energy in the process, maximizing its effect.
g. Vitamin C with Rose Hips

Carlyle Vitamin C Tablets with Rose Hips - Best Vitamin C with Rose Hips
Rose hip is the part of the rose flower just below the petals that contains the rose plant seeds. It has been used for osteoarthritis and contains vitamin C. Vitamin C with rose hip formulations usually include ascorbic acid. Rose hips contain antioxidants like lycopene, phenols, flavonoids, ellagic acid, and vitamin E.h. Ascorbyl Palmitate Vitamin C
Life Extension Ascorbyl Palmitate 500 mg - Ascorbyl Palmitate Vitamin C
Ascorbyl palmitate is a fat-soluble, highly bioavailable version of Vitamin C that has the same qualities as ascorbic acid. It is a free radical scavenger and a powerful antioxidant that protects lipids from peroxidation.3. Types of Vitamin C Supplements
a. Vitamin C Capsules

Capsules are the most popular forms of Vitamin C. They are usually swallowed. If you don’t like swallowing pills or want to mix it into beverages, your best bet is to consider liquid or powdered supplements.
b. Chewable Vitamin C Supplement
NOW Foods’ Chewable C500 - Best Chewable Vitamin C
c. Vitamin C Gummies
Purify Life Vitamin C Gummies - Best Vitamin C Gummies
Gummy vitamins are one of the hottest trends in nutrition supplements. Although gummy vitamins are convenient and taste great, they should not be confused with candy. It’s important that you don’t exceed the recommended dose, as too much vitamin C could lead to unintended side effects. Like other supplements, be sure to store them away from little ones to avoid a potential overdose.
d. Liquid Vitamin C
Liquid supplements are a convenient option for anyone looking for a supplement that can be easily mixed into beverages and absorbed quickly.
e. Vitamin C Powder Supplement
Emergen-C Immune+ - Best Vitamin C Powder
Powdered supplements are a great, flexible option. Whether you plan on drinking them mixed into juices and smoothies or want to fill your own capsules with customized doses, powdered vitamin C is the way to go.
4. Vitamin C and Other Supplements
a. Vitamin C and Quercetin
Incidentally, ascorbic acid (vitamin C) and the bioflavonoid quercetin (originally labeled vitamin P) were both discovered by the same scientist — Nobel prize winner Albert Szent-Györgyi.
On its own, quercetin has a low bioavailability, which means your body absorbs it poorly. Vitamin C helps increase the bioavailability of Quercetin.
Quercetin and vitamin C co-administration exerts a synergistic antiviral action due to overlapping antiviral and immuno-modulatory properties and the capacity of ascorbate to recycle quercetin, increasing its efficacy.
i. COVID-19 (FLCCC I-MASK+ Protocol)
Ascorbic acid (vitamin C) and the bioflavonoid quercetin (originally labeled vitamin P) were both discovered by the same scientist — Nobel prize winner Albert Szent-Györgyi. Quercetin and vitamin C also act as an antiviral drug, effectively inactivating viruses.
Vitamin C is a potent antioxidant, likely immune system optimizer and has been shown to work synergistically with quercetin, likely increasing quercetin’s bioavailability (source). As per Integrative Medicine’s 4th edition, quercetin is a poorly absorbed nutrient but Vitamin C increases the absorption of quercetin and recommends that Quercetin should be blended with Vitamin C (source).
Specifically, there is evidence that vitamin C and quercetin co-administration exerts a synergistic antiviral action due to overlapping antiviral and immunomodulatory properties and the capacity of ascorbate to recycle quercetin, increasing its efficacy (source). It has been shown that Quercetin and Vitamin C markedly inhibited mRNA expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines - as the release of inflammatory cytokines are behind acute respiratory distress syndrome (source). The quercetin and vitamin C combination can prevent the exacerbation of inflammation.
In June 19, 2020, Dr Marik published the paper “Quercetin and Vitamin C: An Experimental, Synergistic Therapy for the Prevention and Treatment of SARS-CoV-2 Related Disease (COVID-19)” in the journal Frontiers in Immunology. The paper presents evidence for the use of vitamin C and quercetin — based on their biological actions and pharmacokinetics profiles — both as prophylaxis in high-risk populations, and as an adjunct to drugs such as Remdesivir or convalescent plasma in the treatment of hospitalized COVID-19 patients.
For updated prevention and early outpatient protocol for COVID-19 positive, please check out FLCCC I-MASK+ protocol.
ii. Vitamin C, Quercetin and Bromelain
Forest Leaf Quercetin 500mg with Bromelain, Vitamin C and Stinging Nettle - Vitamin C with Quercetin and Bromelain
Quercetin was initially found to provide broad-spectrum protection against SARS coronavirus in the aftermath of the SARS epidemic that broke out across 26 countries in 2003. Now, some doctors are advocating its use against SARS-CoV-2, in combination with Bromelain and vitamin C.
Quercetin works best when taken with Vitamin C and Bromelain, as vitamin C helps activate it and bromelain helps with the absorption.
b. Vitamin C and Melatonin
Natrol Sleep+ Immune Health Sleep Aid Gummies > Melatonin Gummies with Vitamin C and Vitamin D
Melatonin and vitamin C are involved with ACE2, the receptor that SARS-CoV-2 uses to gain entry into the cell. Together, melatonin and vitamin C help reduce SARS-CoV-2 virulence by inhibiting NLRP3 inflammasomes, which in turn inhibits cytokine storms.
5. Vitamin C Benefits
a. Vitamin C is an Antioxidant
When free radicals build up in the body, they can cause oxidative stress, which has been related to a variety of chronic illnesses.Antioxidants are molecules that help the body’s immune system function better by defending cells against dangerous molecules known as free radicals. Vitamin C is an antioxidant that can help to boost your body’s natural defenses. It protects the skin from oxidative stress by sequentially donating electrons to neutralize the free radicals. (Source)
b. Vitamin C Helps Lower Blood Pressure
A study suggest that the antihypertensive effect of vitamin C is associated with a reduction in vascular sensitivity to noradrenaline and enhancement of endothelium-dependent relaxation due to increased nitric oxide bioavailability.Another study also suggest that for short-term trials, vitamin C supplementation reduced systolic BP (SBP) and diastolic BP (DBP). Long-term trials on the effects of vitamin C supplementation on BP and clinical events are needed.
i. Vitamin C for Diabetes Type 2
A review of 28 studies (Diabetes Care. 2021 Feb) in 1,574 people with type 2 diabetes mellitus, demonstrated that vitamin C supplementation may improve blood sugar control and blood pressure in people with type 2 diabetes.
c. Vitamin C for the Immune System
Overall, vitamin C appears to exert a multitude of beneficial effects on cellular functions of both the innate and adaptive immune system. Although vitamin C is a potent antioxidant protecting the body against endogenous and exogenous oxidative challenges, it is likely that its action as a cofactor for numerous biosynthetic and gene regulatory enzymes plays a key role in its immune-modulating effects. [Source]Vitamin C also plays a vital role in neutrophil function and thus essential for proper immune system response. It helps white blood cells function more effectively while protecting them from damage by potentially harmful molecules such as free radicals.
i. Does Vitamin C Help With Cold?
.jpg)
Controlled studies have shown that vitamin C shortens and alleviates the common cold and prevents colds under specific conditions and in restricted population subgroups.
A review of 29 studies in 11,306 people demonstrated that regularly supplementing with vitamin C at an average dose of 1–2 grams per day reduced the duration of colds by 8% in adults and 14% in children (PubMed).
The review also demonstrated that regularly taking vitamin C supplements reduced common cold occurrence in individuals under high physical stress like marathon runners and soldiers by up to 50% (PubMed, PubMed).
People who have pneumonia tend to have lower vitamin C levels, and vitamin C supplements have been shown to shorten the recovery time (PubMed, PubMed).
ii. Vitamin C for Sepsis
Additionally, high dose intravenous vitamin C treatment has been shown to significantly improve symptoms in people with severe infections, including sepsis and acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) resulting from viral infections (PubMed, PubMed).
d. Vitamin C for Respiratory Health
Vitamin C deficiency has been linked to a weakened immune system and a higher risk of respiratory infections. Vitamin C has a function in modulating an infectious agent’s resistance. As a result, vitamin C supplementation may be beneficial in preventing and treating pneumonia.Vitamin C intake may also speed up the recovery from a sinus infection, minimize sinus inflammation, and shorten the length of a sinus infection or cold.

High blood pressure, high triglyceride or LDL (bad) cholesterol levels, and low HDL (good) cholesterol levels are factors that raise the risk of heart disease. Vitamin C may assist to lower these risk factors.
A study suggest that high supplemental vitamin C intakes can reduce incidence of major coronary heart disease events.
e. Vitamin C for Heart Health

A study suggest that high supplemental vitamin C intakes can reduce incidence of major coronary heart disease events.
This report shows a strong inverse correlation with blood ascorbic acid levels and all-cause mortality, including cardiovascular disease.
f. Vitamin C for Iron Absorption
Vitamin C intake has been shown to improve iron absorption. It binds non-heme iron and stores it in a form that’s easier for your body to absorb. (Source)g. Vitamin C for Skin Health
i. What Does Vitamin C Do For Skin?
Vitamin C is found at high levels in the epidermis (outer layer of skin) as well as the dermis (inner layer of skin). Its cancer-fighting (antioxidant) properties, and its role in collagen production help keep your skin healthy. This is why vitamin C is one of the key ingredients found in many antiaging skin care products.
ii. Vitamin C for Collagen Synthesis
Vitamin C is important for the formation of collagen. Collagen is a protein that makes up more than 70 percent of the dry weight of your skin. Collagen can also improve skin elasticity, reduce visible wrinkles, tooth health and increase blood flow to the skin. Therefore, collagen helps to heal damaged skin and reduces the appearance of wrinkles.
Adequate vitamin C intake can also help repair and prevent dry skin. An article published in Indian Dermatology Online Journal states that, when applied topically, vitamin C can reverse the signs of photoaging like hyperpigmentation.
iii. Vitamin C Protects From Sun
Vitamin C is also an essential part of the skin’s defense system. Your skin cells use this vitamin to protect from stress caused by pollution, smoking, and UV rays. It’s actively transported to the skin, where it can act as an antioxidant and help strengthen the skin’s barriers (ScienceDirect).
Taking vitamin C orally can enhance the effectiveness of sunscreens applied to your skin for protection from the sun’s harmful UV rays. It does this by decreasing cell damage and helping the healing process of bodily wounds. Studies have also shown that taking vitamin C may shorten the time needed for wounds to heal. (PubMed, PubMed).
h. Vitamin C for Anti-Aging
Vitamin C can help to maintain a proper epigenome, especially in combination with another longevity ingredient, alpha- ketoglutarate.6. Vitamin C Dosage

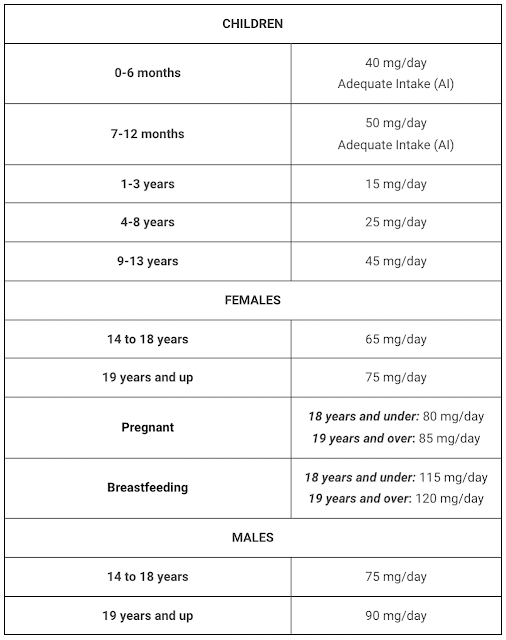
The recommended daily amount of vitamin C for adults is 90 mg for men, 75 mg for women, and up to 120 mg for women who are pregnant or breastfeeding. However, certain medical conditions may require that you take much higher doses (NIH). However, smokers need 35 mg/day more vitamin C than nonsmokers. (Source)
Children have lower vitamin C requirements, which range from 25–75mg per day, depending on their age. However, it’s not generally advised to give children a vitamin C supplement unless their pediatrician has recommended it.
Note that the Tolerable Upper Intake Level (UL) for vitamin C for men, as well as women ages 19 and above, is 2,000 mg. Meanwhile, the UL for children ranges from 400–1,800 mg, depending on age. Daily intakes at or below these amounts are unlikely to result in any adverse health effects (NIH).
Generally, high doses of vitamin C are unnecessary and could contribute to harmful side effects. Only consume high doses if your healthcare provider recommends doing so.
Children have lower vitamin C requirements, which range from 25–75mg per day, depending on their age. However, it’s not generally advised to give children a vitamin C supplement unless their pediatrician has recommended it.
Note that the Tolerable Upper Intake Level (UL) for vitamin C for men, as well as women ages 19 and above, is 2,000 mg. Meanwhile, the UL for children ranges from 400–1,800 mg, depending on age. Daily intakes at or below these amounts are unlikely to result in any adverse health effects (NIH).
Generally, high doses of vitamin C are unnecessary and could contribute to harmful side effects. Only consume high doses if your healthcare provider recommends doing so.
7. Vitamin C Deficiency
Although vitamin C deficiency is rare in developed countries, it can cause serious health problems that, if left untreated, could be fatal. Most people do not take 5 servings of fruits and vegetables on a daily basis. Furthermore, Vitamin C is easily destroyed by heat during cooking and our human bodies are not capable of producing and storing Vitamin C.
a. Risk Factors of Vitamin C Deficiency
Vitamin C levels have been shown to decrease in the elderly population as well as those exhibiting chronic underlying conditions (e.g. diabetes, hypertension).
– Babies only fed cow’s milk
– Seniors only consuming tea and toast diet
– Not getting enough fruits and vegetables
– Smokers : Tobacco smoking (each cigarette oxidizes about 60 mg of vitamin C)
– People with eating disorders
– People with type 1 diabetes who need a lot of vitamin C
– Individuals with disorders of the GI tract like inflammatory bowel disease.
– Individuals with iron overload, which causes the kidneys to waste vitamin C
b. Symptoms of Vitamin C Deficiency
Symptoms of vitamin C deficiency can start to appear after 8 to 12 weeks. Early signs include a loss of appetite, weight loss, fatigue, irritability, and lethargy.
Within 1 to 3 months, there may be signs of..
Within 1 to 3 months, there may be signs of..
- Anemia
- Myalgia, or pain, including bone pain
- Swelling, or edema
- Petechiae, or small red spots resulting from bleeding under the skin
- Corkscrew hairs
- Gum disease and loss of teeth
- Poor wound healing
- Shortness of breath
- Mood changes, and depression (Source)
8. Vitamin C Overdose

Vitamin C is a water soluble vitamin which gets excreted in the urine when consumed in excess.
a. How Much Vitamin C Is Too Much?
In males and females aged 19 years and older, the upper limit for vitamin C consumption is 2,000 mg. For pregnant or nursing women, the restriction stays the same.
We would not recommend taking high dose supplementation of Vitamin C for maintenance purposes. High dose Vitamin C are considered prescription dosage and is meant for 'treatment' and not 'maintenance'. Up to 500 mg/day should be reasonable.
b. Vitamin C Side Effects
Although too much dietary vitamin C is unlikely to be harmful, an overdose of vitamin C supplements might cause..- Diarrhea
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Heartburn
- Abdominal cramps
- Headache
- Insomnia
High dose vitamin C supplements may even cause diarrhea, as they can signal your body to pull water out of the cells and into your digestive tract (NIH).
c. Is Vitamin C Bad for Your Kidneys?
Too much vitamin C in your system can raise the amount of oxalate in your kidneys, which can lead to kidney stones.d. Vitamin C Interactions
i. Copper
Taking large doses of vitamin C (ascorbic acid) on a regular basis lowers your level of copper, so if you are already deficient in copper and take high doses of vitamin C, you can compromise your immune system.
9. Vitamin C Foods
Fruits and vegetables are the best sources of vitamin C. Citrus fruits, tomatoes and tomato juice, and potatoes are major contributors of vitamin C to the American diet. Other good food sources include red and green peppers, kiwifruit, broccoli, strawberries, Brussels sprouts, and cantaloupe. Although vitamin C is not naturally present in grains, it is added to some fortified breakfast cereals.
The vitamin C content of food may be reduced by prolonged storage and by cooking because ascorbic acid is water soluble and is destroyed by heat. Steaming or microwaving may lessen cooking losses.
Fortunately, many of the best food sources of vitamin C, such as fruits and vegetables, are usually consumed raw.
Consuming five varied servings of fruits and vegetables a day can provide more than 200 mg of vitamin C.
Obtaining nutrients from whole foods is always the best approach, but if you have difficulty meeting your nutrition needs for any reason, a supplement may be necessary.
a. Vitamin C Content in Foods
| Food | Serving size | Mg per serving | Percent of 90 mg DV |
| Guava, raw | 1 cup, raw | 377 | 419% |
| Sweet red pepper, raw | 1 cup, raw | 190 | 211% |
| Tomato juice | 1 cup, canned | 170 | 188.9% |
| Orange juice | 1 cup | 124 | 137.8% |
| Sweet green pepper | 1 cup, raw | 120 | 133% |
| Hot green chili pepper, raw | 1 pepper, raw | 109 | 121% |
| Oranges | 1 large fruit | 97.5 | 108.8% |
| Strawberries | 1 cup, sliced | 97.6 | 108% |
| Papaya | 1 small fruit | 95.6 | 106.2% |
| Pink grapefruit juice | 1 cup | 93.9 | 104.3% |
| Broccoli | 1 cup, raw | 81.2 | 90.2% |
| Pineapple chunks | 1 cup, raw | 78.9 | 87.7% |
| Potato | 1 large vegetable | 72.7 | 80.8% |
| Brussels sprouts | 1 cup, raw | 74.8 | 79.8% |
| Kiwifruit | 1 fruit | 64 | 71.1% |
| Mango | 1 cup, raw | 60.1 | 66.7% |
| Cantaloupe | 1 cup | 57.3 | 63.7% |
| Cauliflower | 1 cup, raw | 51.6 | 57.3% |
| Lemon | 1 fruit | 44.5 | 49.4% |
| White grapefruit | ½ medium fruit | 39 | 43.3% |
10. Vitamin C and COVID-19
Vitamin C may be one of the most well-known immune nutrients that protect against immune deficiencies and which supports the prevention and recovery from the common cold and upper-respiratory issues, and also protects your cardiovascular system, eyes, skin, and other parts of your body. Research has found that vitamin C may help to optimize the immune system.
Please take note that the vitamin C dosages given in the hospitals intravenously are different from those over the counter vitamin C supplements. Therefore, when you come across studies on vitamin C, you need to differentiate those that are given intravenously vs oral vitamin C.
Vitamin C and COVID-19
Check out the evidence tracker on vitamin C and COVID-19 from c19vitaminc.com (constantly updated).
Safety: The U.S. Recommended Dietary Allowance (RDA) for vitamin C is 75 to 120 milligrams per day. Taking large doses of vitamin C (ascorbic acid) on a regular basis lowers your level of copper, so if you are already deficient in copper and take high doses of vitamin C, you can compromise your immune system.
While generally considered safe even in high doses, way too much vitamin C — anything above 2,000 milligrams daily—can cause headaches, insomnia, diarrhea, heartburn, and other issues.
Temporarily taking megadoses of vitamin C supplements to combat a case of the cold or flu is likely not going to cause a problem.
Vitamin C, Omicron and Deltacron
Will Vitamin C Work Against Omicron or Deltracron? Vitamin C is not variant specific because it's primary mode of action is to support the body’s immune system which reacts in a variety of ways against viral attack, not just in a specific antibody reaction to a specific spike protein.
Related: Best Vitamin C Supplement
Editor's Note
Although high dose vitamin C appears promising for COVID-19 treatment, these doses were exceptionally high and given via IV — not taken orally. Additionally, it was only given in cases severe enough to require hospitalization.
Your best bet is to eat a diet that’s full of a variety of fruits and vegetables, which naturally provide all the vitamin C a healthy person needs — along with many other nutrients and antioxidants.
Your best bet is to eat a diet that’s full of a variety of fruits and vegetables, which naturally provide all the vitamin C a healthy person needs — along with many other nutrients and antioxidants.
b. FLCCC Protocol
i. Prevention
For prevention, the Front Line COVID-19 Critical Care Working Group (FLCCC) I-MASK+ protocol recommends (updated June 30, 2021):
- Vitamin D3: 1000–3000 IU/day. Note RDA (Recommended Daily Allowance) is 800–1000 IU/day. The safe upper-dose daily limit is likely < 4000 IU/day. Vitamin D deficiency has been associated with an increased risk of acquiring COVID-19 and from dying from the disease. Vitamin D supplementation may therefore prove to be an effective and cheap intervention to lessen the impact of this disease, particularly in vulnerable populations, i.e. the elderly and obese. (Amazon)
- Vitamin C: 500 - 1,000 mg BID (twice daily)
- Quercetin: 250 mg daily. It is likely that vitamin C and quercetin have synergistic prophylactic benefit. Quercetin should be used with caution in patients with hypothyroidism and TSH levels should be monitored. (Amazon)
- Melatonin: 6 mg before bedtime (causes drowsiness). (Amazon)
- Zinc: 30 - 40 mg/day (elemental zinc). Zinc lozenges are preferred. (Amazon)
- Ivermectin prophylaxis dosage (dose for prophylactic ivermectin):
- prevention for high-risk individuals: 0.2 mg/kg per dose (take with or after meals) — one dose today, repeat after 48 hours, then one dose weekly.
- Post COVID-19 exposure prevention: 0.2 mg/kg per dose (take with or after meals) — one dose today, repeat after 48 hours. (Find a Doctor).
Precautionary Note: Ivermectin has a number of potentially serious drug-drug interactions. Please check for potential drug interaction at Ivermectin Drug Interactions - Drugs.com. The most important drug interactions occur with cyclosporin, tacrolimus, anti-retroviral drugs, and certain anti-fungal drugs.
Due to the possible drug interaction between quercetin and ivermectin (may increase ivermectin levels), these drugs should not be taken simultaneously (i.e. should be staggered morning and night).
Ivermectin is also lipophilic and therefore, bioavailability is maximised on a full stomach; or best to be taken with meal.
Related: Best Pulse Oximeter
ii. Early Outpatient Protocol
For early outpatient protocol (COVID-19 positive), the Front Line COVID-19 Critical Care Working Group, FLCCC I-MASK+ protocol recommends (updated June 30, 2021):
- Ivermectin: 0.2–0.4 mg/kg per dose (take with or after meals) — one dose daily, take for 5 days or until recovered. (Find a Doctor). Use upper dose range if: 1) in regions with more aggressive variants; 2) treatment started on or after day 5 of symptoms or in pulmonary phase; or 3) multiple comorbidities/risk factors.
- Fluvoxamine: 50 mg twice daily for 10–14 days. Add to ivermectin if: 1) minimal response after 2 days of ivermectin; 2) in regions with more aggressive variants; 3) treatment started on or after day 5 of symptoms or in pulmonary phase; or 4) numerous co-morbidities/risk factors. Avoid if patient is already on an SSRI (selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor).
- Vitamin D3: 4000 IU/day. (Amazon)
- Vitamin C: 500 - 1,000 mg BID (twice daily) (Amazon)
- Quercetin: 250 mg twice a day. (Amazon)
- Melatonin: 10 mg before bedtime (causes drowsiness). (Amazon)
- Zinc: 100 mg/day. Zinc lozenges are preferred. (Amazon)
- Nasopharyngeal Sanitation: Steamed essential oil inhalation 3 times a day (i.e. vapo-rub) and/or chlorhexidine/benzydamine mouthwash gargles (Amazon) and Betadine nasal spray 2–3 times a day (Amazon).
- Aspirin: 325 mg/day unless contraindicated. (Amazon)
- Pulse Oximeter: FLCCC also recommend monitoring your oxygen saturation with a pulse oximeter and to go to the hospital if you get below 94%. (Amazon)
Editor's Notes:
- Optional: Curcumin: 500 mg twice a day (Ref) (Amazon)
- Duration for supplements: Most supplements (e.g. vitamin D, zinc, quercetin) for early treatment are given for 5 - 10 days. To continue for preventive purposes, dosages will need to be reduced as per the prevention or prophylaxis protocol.
- If you can’t get fluvoxamine (Luvox), using 30mg once a day of fluoxetine (Prozac) is equally effective (equivalent to 50mg twice a day of fluvoxamine).
- Optional: Azithromycin 250 mg twice a day. (Find a Doctor).
c. Zelenko Protocol
Dr Zelenko's prevention protocol recommends the following for COVID-19 prevention for Low and Moderate Risk Patients:
2.1. Quercetin (Amazon) 500mg 1 time a day until a safe and efficacious vaccine becomes available. If Quercetin is unavailable, then use
3. Vitamin D3 5000 iu 1 time a day (Amazon)
11. Online Shopping Guide

a. Best Vitamin C Capsules
Paleovalley Essential C Complex - Best Organic Vitamin C Supplement
Smarter Raw Whole Food Vitamin C - Best Vitamin C Capsule for Face
Viva Naturals Vitamin C - Vitamin C Supplement with Bioflavonoids
Nutra Champs Vitamin C - Vitamin C for Immune Support
Doctor's Best Vitamin C with QC Ascorbic Acid 1000 mg - Best Vitamin C with Ascorbic Acid
Nutrivein Liposomal Vitamin C 1650mg - Best Liposomal Vitamin C
Carlyle Vitamin C Tablets with Rose Hips - Best Vitamin C with Rose Hips
Life Extension Ascorbyl Palmitate 500 mg - Ascorbyl Palmitate Vitamin C
Nature Made Super B Complex with Vitamin C - Vitamin C with Vitamin B
Pure Encapsulations Magnesium - Vitamin C with Magnesium
PURELY Beneficial Resveratrol - Vitamin C with Resveratrol
Zenwise Green Tea Extract - Vitamin C with Green Tea
Nature's Bounty Immune 24 Hour - Vitamin C with Zinc
Dacha Natural Liposomal Vitamin C - Liposomal Vitamin C
i. Vitamin C with Quercetin
Natural Factors, Bioactive Quercetin - Calcium Ascorbate Vitamin C with Quercetin
Whole Food Quercetin Plus - Best Vitamin C with Quercetin
BlueBonnet Super Quercetin - Vitamin C with Quercetin and Bromelain
Forest Leaf Quercetin - Vitamin C with Quercetin and Bromelain
Vitaraw Quercetin - Vitamin C with Quercetin and Zinc
ii. Multivitamins
Centrum Wellness Packs - Multivitamins with Vitamin C
Nature Made Multi For Him 50+ - Multivitamin with Vitamin C for Men Over 50
Nature Made Multi For Her 50+ - Multivitamin with Vitamin C for Women Over 50
b. Best Chewable Vitamin C Supplement
NOW Foods’ Chewable C500 - Best Chewable Vitamin C
WonderLabs Zinc Lozenges with Vitamin C - Chewable Vitamin C with Zinc
c. Best Vitamin C Gummies
Purify Life Vitamin C Gummies - Best Vitamin C Gummies
Natrol Sleep+ Immune Health Sleep Aid Gummies > Melatonin Gummies with Vitamin C and Vitamin D
Carlyle Vitamin C and Zinc Gummies - Vitamin C and Zinc Gummies
i. Quercetin Chewables for Kids
Joyli Quercetin Gummies - Quercetin Gummies for Kids with Vitamin C, Bromelain and Zinc
Care 4 Harmony Chewable Quercetin - Quercetin Chewables for Kids with Vitamin C and D3
d. Best Liquid Vitamin C
JoySpring C Vitamin plus Zinc - Best Liquid Vitamin C Supplement
Pure Encapsulations’ Liposomal Vitamin C - Vitamin C Liposomal Liquid
e. Best Vitamin C Powder Supplement
NOW Supplements, Sodium Ascorbate Powder - Sodium Ascorbate Vitamin C
Emergen-C Immune+ - Best Vitamin C Powder
Related:




.png)
.png)

.jpg)

.png)


Comments