Chlorella vs Spirulina Comparison 2022

Contents
1. What is Chlorella?
2. What is Spirulina?
3. Chlorella vs Spirulina
4. Chlorella and Spirulina Benefits
5. How Much Chlorella and Spirulina Should I Take
6. Chlorella and Spirulina Supplements
7. Who Should Not Take Spirulina and Chlorella?
8. Chlorella and Spirulina Side Effects
Chorella supplementation, according to researchers, may help the body remove toxins, as well as enhance cholesterol and blood sugar levels, among other health benefits.
Oral Chlorella supplementation (6 g/day) for 12–18 weeks decreased markers of anemia in a group of 32 women in their second and third trimesters of pregnancy, indicating that Chlorella supplementation considerably lowers the risk of pregnancy-associated anemia.
Several clinical trials also indicated that Spirulina has positive effects in managing metabolic syndrome components.
Spirulina contains several active ingredients, notably phycocyanin and β-carotene that have potent antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities. (Source)
From the table above, we can conclude that both protein, carbohydrate, and fat compositions are quite similar. But there are significant nutritional variances in their calorie, vitamin, and mineral amounts.
Chlorella has a high concentration of omega-3 fatty acids, vitamin A, riboflavin, iron, and zinc. Spirulina has more thiamine, copper, and potentially more protein.

Antioxidants are molecules that may protect your cells against free radicals, which has been linked to heart disease, cancer and other diseases. Antioxidants protect tissue from free radical damage by inhibiting radical production, scavenging radicals, or encouraging their decomposition.
Studies have shown that both Spirulina and Chlorella are great antioxidants.
A study evaluated the effect of spirulina intervention on oxidative stress, antioxidant status, and lipid profile of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) patients. They found that the antioxidant status and lipid profile of COPD patients are proven to be improved through an interventional 2 months course of spirulina. Oxidative stress is shown to be reduced as a result of spirulina intervention.
A study found that chlorella supplementation resulted in the conservation of plasma antioxidant nutrient status and improvement in erythrocyte antioxidant enzyme activities in subjects.
Another study also suggests spirulina may have anti-cancer properties. A first report of the in vivo chemopreventive effect of Spirulina platensis against dibutyl nitrosamine(DBN)-induced rat liver cytotoxicity and carcinogenesis, suggesting its potential use in chemoprevention of cancer.

Both Spirulina and Chlorella may help you with weight management.
Chlorella appears to have good health benefits on slightly hypercholesterolemic subjects’ blood lipid profiles, at least in part by improving serum carotenoid profiles. According to one study, the possible effects of Chlorella on serum lipids might be caused by a suppression of intestinal lipid absorption attributable to increased levels of highly polar carotenoids from Chlorella. However, further studies are required to determine this finding.
Another study found that consuming Spirulina maxima on a regular basis for three months improves BMI and weight. Furthermore, it improves blood pressure and endothelial function in overweight patients with hypertension.
According to one study, taking 2–8 grams of spirulina per day can improve lipid profiles, promote weight loss, and lower body mass index (BMI).
• Spirulina Tablets 1000mg | NOW Supplements, Certified Organic Spirulina Tablet 1000 mg
• Spirulina Powder | Natural Elements Organic Spirulina Powder
• Spirulina Powder | SYMNUTRITION Organic Spirulina Powder
• Chlorella Tablets 3000mg (per serving) | Organic Chlorella Tablets, 3000mg Per Serving, 720 Tabs
• Chlorella Powder | Micro Ingredients Organic Chlorella Powder
• Chlorella and Spirulina Tablets | Actif 100% Ocean Cleaned Organic Chlorella and Spirulina
• Chlorella and Spirulina Powder | Amazing Grass Greens Blend Superfood: Super Greens Powder with Spirulina, Chlorella, Beet Root Powder, Digestive Enzymes & Probiotics, Berry
Multiple sclerosis (MS), lupus (systemic lupus erythematosus, SLE), rheumatoid arthritis (RA), pemphigus vulgaris (a skin ailment), and others are autoimmune illnesses. The immune system may become more active as a result of blue-green algae, which might worsen the symptoms of auto-immune diseases. It’s advised to avoid utilizing blue-green algae if you have one of these diseases.
ii. Surgery
Blue-green algae may reduce blood sugar levels during surgery. Best to stop using blue-green algae at least 2 weeks before a scheduled surgery.
iii. Thin blood/bleeding condition
Spirulina has an anticoagulant effect, which means it thins your blood and makes it take longer for blood to clot. If you have a bleeding condition or are using blood thinners, you should avoid spirulina.
Iodine allergies should avoid chlorella supplements since some of them include iodine. Best to inform your doctor about any supplements you are taking.
Allergic Reaction: asthma and other respiratory issues.
Sun sensitivity on the skin (photosensitivity)
Diarrhea
Nausea
Gas (flatulence)
Green stool
Cramping in the stomach (especially in the first week of use)
Other adverse effects may occur, which are not listed in this article. If you have any questions concerning side effects, talk to your doctor.
Upset stomach
Increased gas
Swelling
Tiredness
Headache
Feeling dizzy
When do I need to call the doctor?
Severe reaction, such as wheezing; tightness in the chest; fever; itching; bad cough; blue skin color; seizures; swelling of face, lips, tongue, or throat. This is not a complete side effects, if you have other concerning side effect, go to the emergency room right away.
Symptoms of a liver issue. These include stomach pains or vomiting, fatigue, dark urine, yellow skin or eyes, and a lack of appetite.
You May Be Interested In..
Spirulina vs chlorella vs chlorophyll
2. What is Spirulina?
3. Chlorella vs Spirulina
4. Chlorella and Spirulina Benefits
5. How Much Chlorella and Spirulina Should I Take
6. Chlorella and Spirulina Supplements
7. Who Should Not Take Spirulina and Chlorella?
8. Chlorella and Spirulina Side Effects
1. What is Chlorella?
Chlorella is a green, unicellular alga that contains various nutrients. There are around 30 different species of chlorella, but the two most often used in research are Chlorella vulgaris and Chlorella pyrenoidosa.Chorella supplementation, according to researchers, may help the body remove toxins, as well as enhance cholesterol and blood sugar levels, among other health benefits.
a. What Nutrients Are in Chlorella?
Chlorella products contain large amount of good quality protein, dietary fibers, and polyunsaturated fatty acids, such as α-linolenic and linoleic acids. Chlorella products, in particular, contain vitamins D2 and B12, which are not found in plant-based diets, as well as higher levels of folate and iron than other plant-based foods.Oral Chlorella supplementation (6 g/day) for 12–18 weeks decreased markers of anemia in a group of 32 women in their second and third trimesters of pregnancy, indicating that Chlorella supplementation considerably lowers the risk of pregnancy-associated anemia.
2. What is Spirulina?
Spirulina, also known as Arthrospira platensis is a blue-green alga which also has many nutrients. It includes phycocyanin, a strong plant-based protein. This has antioxidant, pain-relieving, anti-inflammatory, and brain-protective properties, according to research.Several clinical trials also indicated that Spirulina has positive effects in managing metabolic syndrome components.
a. What Nutrients Are in Spirulina?
In humans, this alga provides an important staple food with any significant side effects. Apart from the high protein content (up to 70%), it also contains vitamins, particularly B12 and provitamin A (-carotenes), as well as minerals, especially iron. It also contains phenolic acids, tocopherols, and -linolenic acid in abundance. Since spirulina lacks cellulose cell walls, it is easily digestible. (Source)Spirulina contains several active ingredients, notably phycocyanin and β-carotene that have potent antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities. (Source)
3. Chlorella vs Spirulina
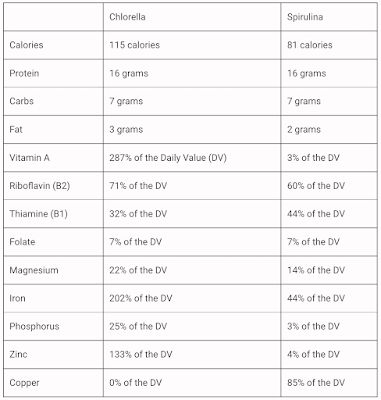
A 1-ounce (28-gram) serving of these algae contains the following (Source, Source):
From the table above, we can conclude that both protein, carbohydrate, and fat compositions are quite similar. But there are significant nutritional variances in their calorie, vitamin, and mineral amounts.
Chlorella has a high concentration of omega-3 fatty acids, vitamin A, riboflavin, iron, and zinc. Spirulina has more thiamine, copper, and potentially more protein.
4. Chlorella and Spirulina Benefits
a. Antioxidant Effects

Antioxidants are molecules that may protect your cells against free radicals, which has been linked to heart disease, cancer and other diseases. Antioxidants protect tissue from free radical damage by inhibiting radical production, scavenging radicals, or encouraging their decomposition.
Studies have shown that both Spirulina and Chlorella are great antioxidants.
Spirulina and Antioxidant Effects
C-Phycocyanin (C-PC) is one of the major biliproteins of Spirulina with antioxidant and radical scavenging properties.A study evaluated the effect of spirulina intervention on oxidative stress, antioxidant status, and lipid profile of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) patients. They found that the antioxidant status and lipid profile of COPD patients are proven to be improved through an interventional 2 months course of spirulina. Oxidative stress is shown to be reduced as a result of spirulina intervention.
Chlorella and Antioxidant Effects
Chlorella contains chlorophyll, vitamin C, beta-carotene, lycopene and lutein, which are considered antioxidants. A study found that chlorella supplementation resulted in the conservation of plasma antioxidant nutrient status and improvement in erythrocyte antioxidant enzyme activities in subjects.
b. Anti Cancer Effect
Chlorella and Spirulina May Have Anticancer Effects
A study showed that chlorella vulgaris may have anti-cancer effects by inducing apoptosis signaling cascades via an increased expression of P53, Bax and caspase-3 proteins and through a reduction of Bcl-2 protein, which subsequently lead to increased DNA damage and apoptosis. Another study also suggests spirulina may have anti-cancer properties. A first report of the in vivo chemopreventive effect of Spirulina platensis against dibutyl nitrosamine(DBN)-induced rat liver cytotoxicity and carcinogenesis, suggesting its potential use in chemoprevention of cancer.
c. Cardiovascular Health
High blood pressure and high cholesterol levels are two of the most important risk factors in atherosclerosis, the leading cause of heart attacks. Maintaining and monitoring your cholesterol levels and your blood pressure will help lower your risk for heart disease.Spirulina and Cholesterol-Lowering Effects
Ramamoorthy and Premakumari in a more recent study administered Spirulina supplements in ischemic heart disease patients and found a significant reduction in blood cholesterol, triglycerides and LDL cholesterol and an increase in HDL cholesterol.Chlorella and Antihypertensive Effects
A study concluded that Chlorella supplementation improves total cholesterol levels, low-density lipoprotein cholesterol levels, systolic blood pressure, diastolic blood pressure, and fasting blood glucose levels.d. Effects on Diabetes
Patients with type 2 diabetes have high blood glucose levels, insulin resistance, and low insulin sensitivity, which can lead to significant complications.Spirulina and Diabetes
A study aimed to evaluate the hypoglycemic and hypolipidemic role of Spirulina, showed that Spirulina supplementation can help people with type 2 diabetes control their blood sugar levels and improve their lipid profile.Chlorella and Diabetes
Another study was conducted in 28 borderline-diabetic participants treated with either Chlorella (8 g/day) or placebo for 12 weeks. They found that the mRNA expression level of resistin, an insulin resistance inducer, was significantly lower in the Chlorella group than in the placebo group and correlated with the expression levels of hemoglobin A1c, tumor necrosis factor-a, and interleukin-6, all of which are involved in glucose metabolism and/or inflammation.e. Weight Loss

Both Spirulina and Chlorella may help you with weight management.
Chlorella Benefits for Weight Loss
Chlorella may have an effect on how fat cells behave in the body, therefore it may help with weight loss.Chlorella appears to have good health benefits on slightly hypercholesterolemic subjects’ blood lipid profiles, at least in part by improving serum carotenoid profiles. According to one study, the possible effects of Chlorella on serum lipids might be caused by a suppression of intestinal lipid absorption attributable to increased levels of highly polar carotenoids from Chlorella. However, further studies are required to determine this finding.
Spirulina Benefits for Weight Loss
According to a study, spirulina platensis, as a supplemental therapy, may help with adherence to restricted-calorie diet, weight loss management, and triglyceride reduction via modulating anti-inflammatory pathways.Another study found that consuming Spirulina maxima on a regular basis for three months improves BMI and weight. Furthermore, it improves blood pressure and endothelial function in overweight patients with hypertension.
f. Detoxification
Both algae have been shown to be successful in detoxification; they may be used in high dosages for heavy metal detox, binding toxins and purging them from the body, frequently without the usual detoxification side effects.5. How Much Chlorella and Spirulina Should I Take?
a. How Much Chlorella Should I Take?
Always check the label on your dietary supplement. Usually, adults take 2-3 grams by mouth daily for up to 3 months.b. How Much Spirulina Should I Take?
Spirulina is usually taken in doses of 1–3 grams per day, however doses of up to 10 grams per day have been found to be helpful.According to one study, taking 2–8 grams of spirulina per day can improve lipid profiles, promote weight loss, and lower body mass index (BMI).
6. Spirulina and Chlorella Supplements
a. Best Spirulina Supplements
• Spirulina Tablets 500mg | Nutrex Hawaii, Pure Hawaiian Spirulina Tablet 500 mg• Spirulina Tablets 1000mg | NOW Supplements, Certified Organic Spirulina Tablet 1000 mg
• Spirulina Powder | Natural Elements Organic Spirulina Powder
• Spirulina Powder | SYMNUTRITION Organic Spirulina Powder
b. Best Chlorella Supplements
• Chlorella Tablets 500mg | Sun Chlorella 500mg Whole Body Wellness Green Algae Superfood Supplement• Chlorella Tablets 3000mg (per serving) | Organic Chlorella Tablets, 3000mg Per Serving, 720 Tabs
• Chlorella Powder | Micro Ingredients Organic Chlorella Powder
c. Best Spirulina and Chlorella Supplements
• Chlorella and Spirulina Capsules | Vimerson Health Spirulina Chlorella 60 Vegetarian Capsules• Chlorella and Spirulina Tablets | Actif 100% Ocean Cleaned Organic Chlorella and Spirulina
• Chlorella and Spirulina Powder | Amazing Grass Greens Blend Superfood: Super Greens Powder with Spirulina, Chlorella, Beet Root Powder, Digestive Enzymes & Probiotics, Berry
7. Who Should Not Take Spirulina and Chlorella?
a. Who Should Not Take Spirulina?
i. Autoimmune diseaseMultiple sclerosis (MS), lupus (systemic lupus erythematosus, SLE), rheumatoid arthritis (RA), pemphigus vulgaris (a skin ailment), and others are autoimmune illnesses. The immune system may become more active as a result of blue-green algae, which might worsen the symptoms of auto-immune diseases. It’s advised to avoid utilizing blue-green algae if you have one of these diseases.
ii. Surgery
Blue-green algae may reduce blood sugar levels during surgery. Best to stop using blue-green algae at least 2 weeks before a scheduled surgery.
iii. Thin blood/bleeding condition
Spirulina has an anticoagulant effect, which means it thins your blood and makes it take longer for blood to clot. If you have a bleeding condition or are using blood thinners, you should avoid spirulina.
b. Who Should Not Take Chlorella?
Warfarin and other blood-thinning medications may have a tougher time working if you eat chlorella.Iodine allergies should avoid chlorella supplements since some of them include iodine. Best to inform your doctor about any supplements you are taking.
8. Chlorella and Spirulina Side Effects
a. Chlorella Side Effects
Side effects of chlorella include:Allergic Reaction: asthma and other respiratory issues.
Sun sensitivity on the skin (photosensitivity)
Diarrhea
Nausea
Gas (flatulence)
Green stool
Cramping in the stomach (especially in the first week of use)
Other adverse effects may occur, which are not listed in this article. If you have any questions concerning side effects, talk to your doctor.
b. Spirulina Side Effects
Side effects of spirulina include:Upset stomach
Increased gas
Swelling
Tiredness
Headache
Feeling dizzy
When do I need to call the doctor?
Severe reaction, such as wheezing; tightness in the chest; fever; itching; bad cough; blue skin color; seizures; swelling of face, lips, tongue, or throat. This is not a complete side effects, if you have other concerning side effect, go to the emergency room right away.
Symptoms of a liver issue. These include stomach pains or vomiting, fatigue, dark urine, yellow skin or eyes, and a lack of appetite.
You May Be Interested In..
Spirulina vs chlorella vs chlorophyll
.png)
.png)
.jpg)
.png)






Comments