Immune Support: Quercetin, Vitamin C, Zinc, Vitamin D3
The Front Line COVID-19 Critical Care Alliance (FLCCC) and other healthcare organizations have incorporated a mix of readily available agents into their management protocol for COVID-19.
Quercetin and COVID-19
Quercetin was initially found to provide broad-spectrum protection against SARS coronavirus in the aftermath of the SARS epidemic that broke out across 26 countries in 2003. Now, some doctors are advocating its use against SARS-CoV-2, in combination with vitamin C, noting that the two have synergistic effects. It is also a flavonoid and antioxidant that may help to reduce inflammatory cytokines, infections, allergies and anti-blood clot property. Research has found that quercetin may be particularly beneficial for viral respiratory infections.
.png)
Quercetin is a zinc ionophore (J Agric Food Chem. 2014). A 2015 study found that that Quercetin shows inhibitory activity in the early stages of a wide range of influenza viruses, including H1N1 and H5N1 (Viruses 2016). Although influenza is not in the same family of viruses as the coronavirus, it’s plausible that a similar mechanism could apply here. There is actually some evidence that Quercetin has already proven effective at treating Ebola and Zika viruses.
- Quercetin should be used with caution in patients with hypothyroidism (low thyroid hormone) and relevant thyroid hormone levels should be monitored.
- Quercetin and ivermectin interactions? According to Drugs.com: "No interactions were found between ivermectin and Quercetin. This does not necessarily mean no interactions exist. Always consult your healthcare provider." Due to a possible interaction between quercetin and ivermectin, these drugs should not be taken simultaneously (i.e., should be staggered at different times of day).
Vitamin D3 - Anti-inflammatory and Anti-coagulant
“Each 10 ng/mL increase in vitamin D levels was associated with a 45 % and 26 % lower risk of 45-day mortality (HR: 0.55, 95 % CI: 0.40–0.74) and ICU mortality due to COVID-19 (HR: 0.74, 95 % CI: 0.60–0.92), respectively.”
Since the outbreak of the pandemic, many vitamin D sufficiency studies
have been conducted. Almost all of them show that an adequate vitamin D
level reduces the chance of (a) getting ill, (b) ending up in the
hospital, and (c) dying.
Almost all studies consider a
vitamin D blood serum level of >30 ng/mL ‘adequate/good’. Several
studies have shown that people with a blood serum level of >50 ng/mL
hardly get sick at all. Results of a systematic review and meta-analysis
(Nutrients 2021) suggested that COVID-19 mortality risk correlates inversely with
vitamin D3 status, and a mortality rate close to zero could theoretically be achieved at 50 ng/ml 25(OH)D3.
Zinc - Anti-viral
Improving zinc intake/zinc status improves/modulates/enhances immune function. The flip side is, while some aspects of immunity slow, others increase. Uncontrolled immune responses drive excess inflammation. Zinc helps to balance all of this.
“Zinc is involved in numerous aspects of cellular metabolism. It is required for the catalytic activity of approximately 100 enzymes and it plays a role in immune function, protein synthesis, wound healing, DNA synthesis, and cell division. Zinc also supports normal growth and development during pregnancy, childhood, and adolescence and is required for proper sense of taste and smell.”
.png)
Excessive doses may interfere with copper absorption, which could negatively affect your immune system as it can cause copper deficiencies, blood disorders and potentially permanent nerve damage. Zinc can also impair the absorption of antibiotics, and use of zinc nasal gels or swabs has been linked to temporary or permanent loss of smell.
There are several types of zinc supplements. Supplements contain several forms of zinc, including zinc gluconate, zinc citrate and zinc picolinate. The percentage of elemental zinc varies by form. To find out the percentage of elemental zinc in each form, check out elemental zinc percentage.
Vitamin C - Anti-inflammatory
Vitamin C, which most of us reach for with any cold or flu, was used
in high doses to great effect by COVID-19 early treatment doctors.
Vitamin C may be one of the most well-known immune nutrients
that protect against immune deficiencies and which supports the
prevention and recovery from the common cold and upper-respiratory
issues, and also protects your cardiovascular system, eyes, skin,
and other parts of your body. Research has found that vitamin C may
help to optimize the immune system.
Do take note that the vitamin C dosages given in the hospitals
intravenously are different from those over the counter vitamin C
supplements. Therefore, when you come across studies on vitamin C,
you need to differentiate those that are given intravenously vs oral
vitamin C.
Vitamin C and COVID-19
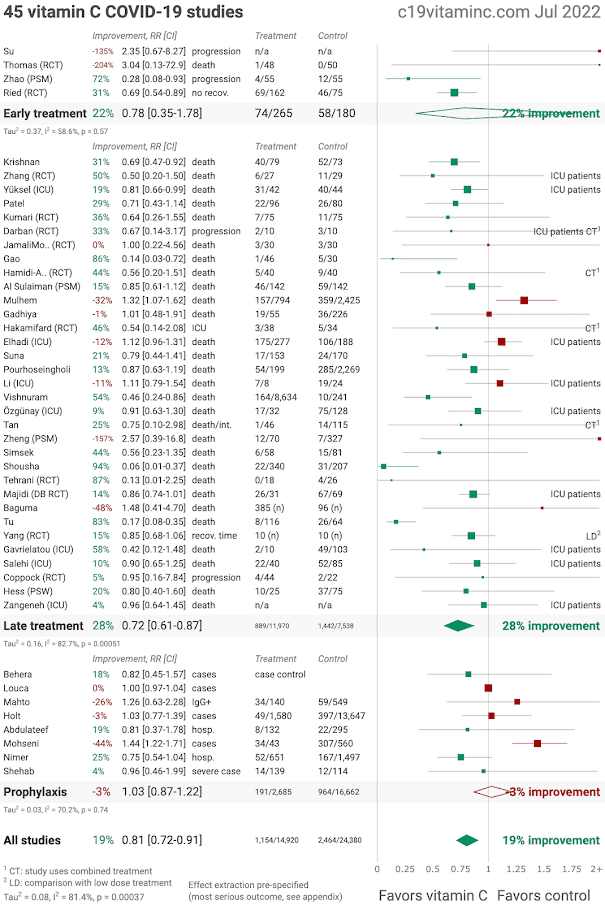
Check out the evidence tracker on vitamin C and COVID-19
from c19vitaminc.com (constantly updated).
Safety: The U.S. Recommended Dietary Allowance (RDA)
for vitamin C is 75 to 120 milligrams per day. Taking large doses
of vitamin C (ascorbic acid) on a regular basis lowers your level
of copper, so if you are already deficient in copper and take high
doses of vitamin C, you can compromise your immune system.
While generally considered safe even in high doses, way too much
vitamin C — anything above 2,000 milligrams daily—can cause
headaches, insomnia, diarrhea, heartburn, and other issues.
Temporarily taking megadoses of vitamin C supplements to
combat a case of the cold or flu is likely not going to cause a
problem.
Many vitamin C supplements that are above the US RDA are sold in the
market. It’s important to seek a physician’s advice if you intend to
take high dose vitamin C on a long term basis. To be on the safe
side, you may also request for your kidney functions to be
monitored.
For long-term, daily use, your best bet is to eat a diet that is
full of high quality organic vegetables and fruits that are
minimally processed. Not only will you get vitamin C, but you will
get all the other accessory nutrients and micronutrients that are
needed to optimize it.
Vitamin C, Omicron and Deltacron
Will Vitamin C Work Against Omicron or Deltracron? Vitamin C is
not variant specific because it's primary mode of action is to
support the body’s immune system which reacts in a variety of ways
against viral attack, not just in a specific antibody reaction to
a specific spike protein.
Related: Best Vitamin C Supplement

Temporarily taking megadoses of vitamin C supplements to combat a case of the cold or flu is likely not going to cause a problem.
Quercetin, Vitamin C, Zinc and Vitamin D3
FLCCC Alliance

As a group of highly published leaders in critical care with expertise in therapies directed at severe infections, in particular “HAT” therapy first developed by Dr. Paul Marik for the treatment of bacterial sepsis, and along with published high patient survival rates from our centers, we were contacted by equally concerned and motivated colleagues from other specialties.
With the increasing publications in addition to our rapidly accumulating personal clinical experiences and investigations into the pathophysiology of COVID-19 patients, we formulated the MATH+ Hospital Treatment Protocol in March 2020. On August 5, 2020, we published our findings in the rationale paper Scientific Review of COVID-19 and MATH+.
Based on these findings, the FLCCC team has developed the I-MASK+ protocol for prophylaxis and at home treatment of early stage disease.
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.jpg)





Comments